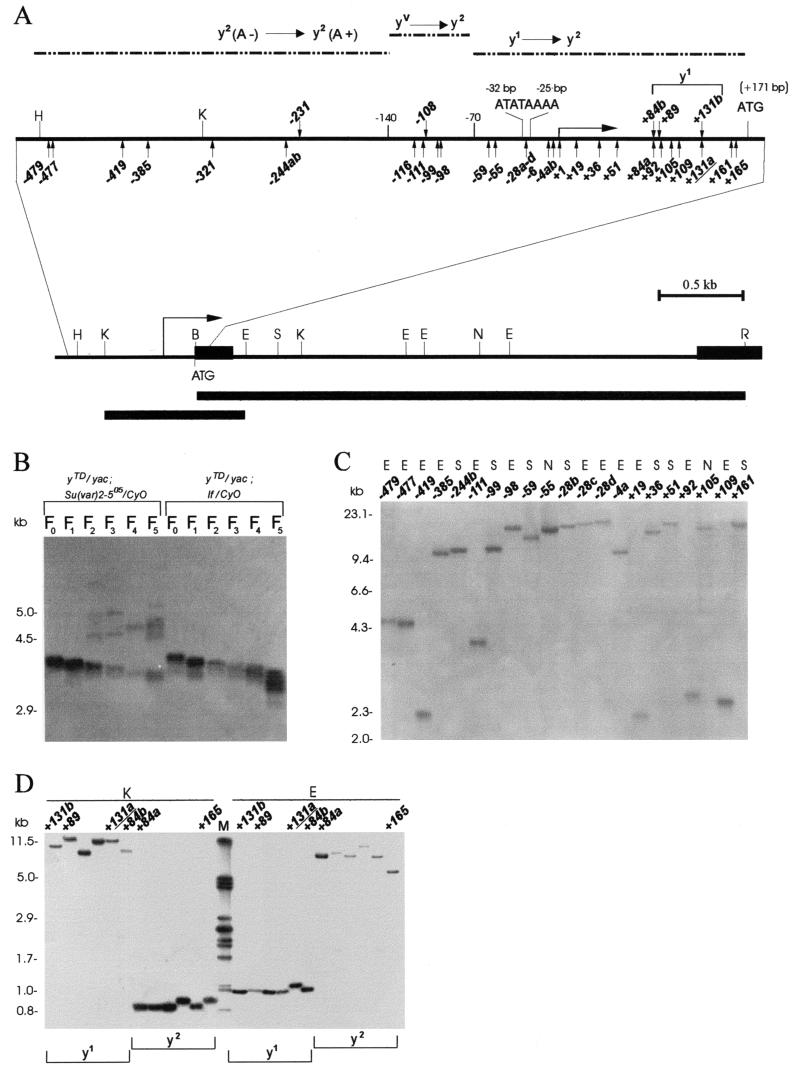
FIG. 1.
Molecular structure of the broken chromosome end in the yellow gene. (A) A schematic presentation of terminal yellow deficiencies associated with different y phenotypes. The promoter (ATATAAAA) and start of translation (ATG) locations are indicated relative to the transcription start site of the yellow gene. The coding yellow region is shown as a black box. The location of the start of the yellow transcription region is shown by a horizontal arrow on the uppermost solid horizontal line. The dotted horizontal lines show the regions of the yellow sequence in which the termini of the yTD line that correspond to the same classes of y phenotype have been mapped. The KpnI-EcoRV and BamHI-EcoRI genomic fragments used as a probe for Southern blot analysis are indicated by the bottommost thick horizontal line and the line just above, respectively. The points of HeT-A attachment are shown by small vertical arrows below the uppermost solid horizontal line. The points of TART attachment are shown by small vertical arrows above the same line. Restriction enzyme abbreviations: B, BamHI; K, KpnI; H, HindIII; E, EcoRV; N, NruI; S, SpeI; R, EcoRI. (B) Effect of the Su(var)2-505 mutation on the rate of terminal DNA shortening. Southern blot analysis of DNAs prepared from 10 to 14 yTD/yac females of the Su(var)2-505 and control lines taken in six subsequent generations as described in the Fig. 2A legend. DNAs were digested with EcoRI. The filter was hybridized with the BamHI-EcoRI probe. The additional bands correspond to new DNA attachments to the receding yellow sequences at the end of truncated chromosome. (C) HeT-A and TART transpositions to the broken chromosome end in the yellow gene. DNAs were digested with EcoRV (E), NruI (N), and SpeI (S). The filter was hybridized with the KpnI-EcoRV probe. (D) HeT-A and TART transpositions obtained in the progeny of one yTD/yac; Su(var)2-505/CyO female displaying a y1 phenotype. In the next generation, all yTD/yac; If/CyO daughters with either a y1- or a y2-like phenotype were individually crossed for DNA isolation. DNAs were digested with KpnI (K) and EcoRV (E). The filter was hybridized with the KpnI-EcoRV probe. The junctions between yellow and new DNA attachments were cloned and sequenced in the cases designated with numbers (see Fig. 3).