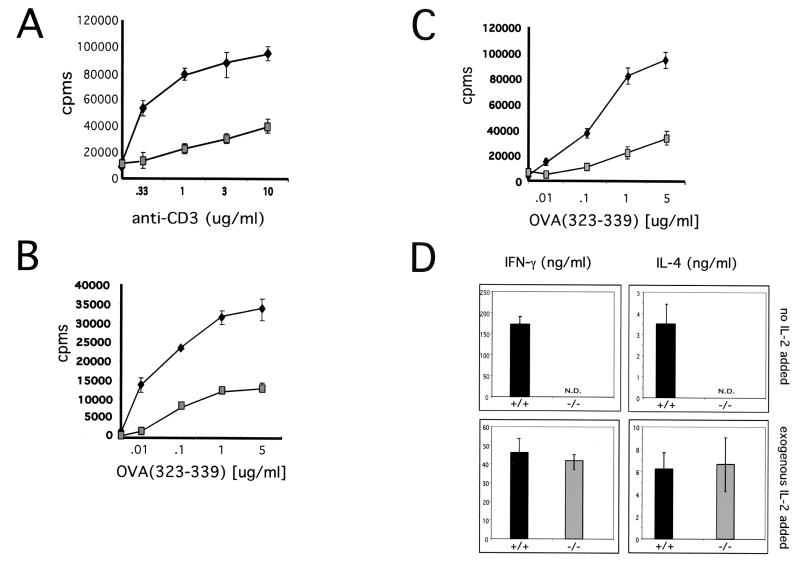
FIG. 5.
KSR−/− T cells display an activation defect ex vivo in response to physiologic antigen. (A) Defective T-cell proliferation in response to anti-CD3. 2C11 was used to stimulate splenic T cells from wild-type or KSR−/− mice. T-cell proliferation was measured by quantitation of [3H]thymidine incorporation. (B) KSR+/− or KSR−/− T cells transgenically expressing the DO11.10 TCR were used for proliferation assays in response to ovalbumin peptide (amino acids 323 to 339). After 24 h, cells were pulsed with [3H]thymidine for 12 h, and [3H]thymidine incorporation was measured. (C) IL-2 release was measured by using the IL-2-dependent cell line CTLL-2. After 24 h, supernatants from proliferating KSR+/− or KSR−/− T cells were used to stimulate CTLL-2 proliferation. (D) Th1/Th2 effector differentiation was studied by using wild-type and KSR−/− T cells under conditions which promote Th1 or Th2 development (top). Exogenous IL-2 was added to compensate for the proliferation defect of KSR−/− T cells (bottom).