FIG. 2.
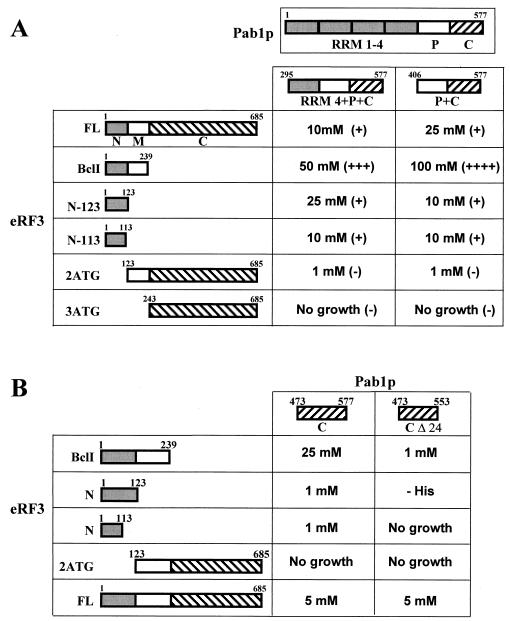
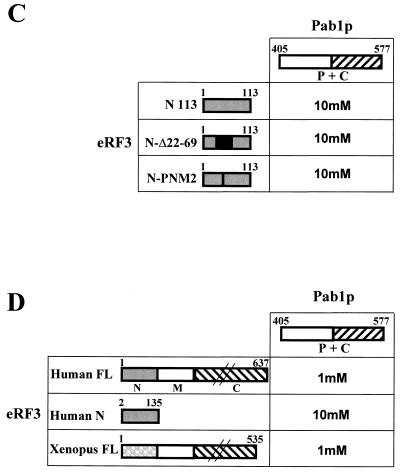
The N+M part of eRF3 interacts with the C part of yeast Pab1 protein. (A) Two-hybrid interactions. Strain L40 carrying different PAB1 deletions in pBTM116 plasmid (69) was transformed with pGADGH/SUP35 (FL), pGADGH/SUP35-Bcl (BclI), pGADGH/SUP35-N123 (N123), pGADGH/SUP35-2ATG (2ATG), pGADGH/SUP35-3ATG (3ATG) (see Materials and Methods), and pACT2/SUP35N (N113) (4). The interactions were tested by the extent of resistance to 3-AT and by an X-Gal filter-lifting assay. Symbols for β-galactosidase assay: ++++, very strong; +++, strong; ++, moderate; +, weak; −, no activity. For the 3-AT assay the highest concentration of 3-AT that still allowed yeast cell growth is noted. Extent of β-galactosidase activity is shown in parentheses. At least five independent transformants were tested in each case. (B) Minimal domain of Pab1p participating in the interaction with yeast eRF3. Strain HF7C was cotransformed with pGADGH/SUP35 (FL), pGADGH/SUP35-Bcl (BclI), pGADGH/SUP35-N123 (N123), pGADGH/SUP35-2ATG (2ATG), pACT2/SUP35N (N113), pGBT9/PAB1 C (C), and pGBT9/PAB1 CΔ24 (ΔC24). The extent of 3-AT resistance is shown; −His corresponds to the growth on His− medium. (C) Minimal domain of eRF3 participating in the interaction with the C-terminal domain of Pab1p. Strain HF7C bearing pGADGH/PAB1 P+C plasmid was transformed with pAS-SUP35N (N113), pAS-SUP35N (N113) Δ22-69 (N-Δ22-69), or pAS/SUP35N-PNM2 (N-PNM2). The interactions were tested in the same way as for panel B. (D) Interactions of yeast Pab1p with human and Xenopus eRF3 in the two-hybrid system. Strain HF7C bearing pGADGH/PAB1 P+C plasmid was transformed with plasmids pGBT9/hGSPT1 (human FL), pAST-eRF3 h-N (human N), and pGBT9/xeRF3 (Xenopus FL), and the resulting cotransformants were assayed for interactions in the same way as for panel B.