FIG. 5.
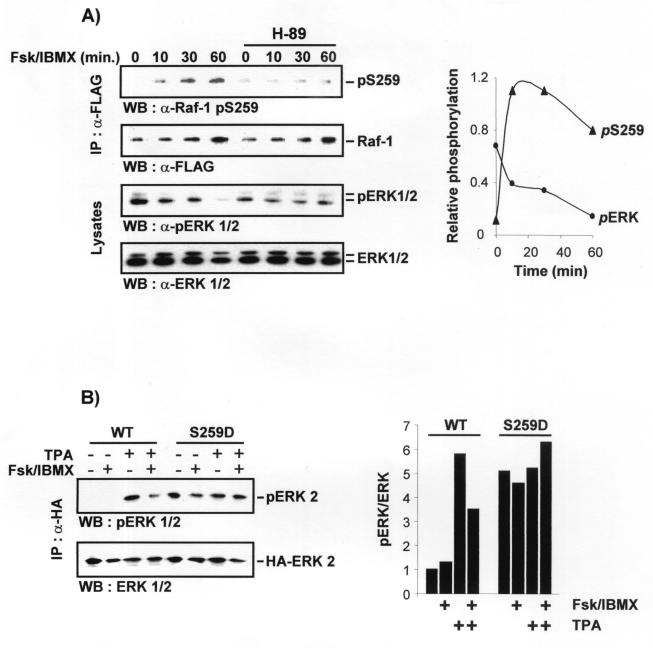
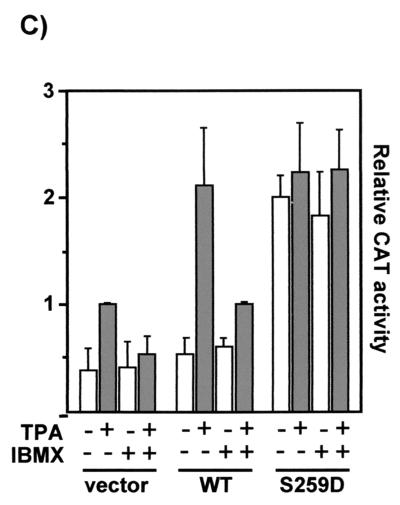
cAMP inhibits the ERK pathway at the level of Raf-1 through the induction of the phosphorylation of serine 259 in Raf-1. (A) RafS259-stimulated ERK activity is resistant to inhibition by cAMP. COS-1 cells were transfected with HA-ERK-2 plus pCMV5Raf-1 or pCMV5RafS259D. Cells were serum starved and treated with forskolin and IBMX as in Fig. 4. HA-ERK-2 was immunoprecipitated with an HA antibody, and activated ERK was detected by immunoblotting with a phosphospecific ERK antibody (upper panel). The blot was stripped and subsequently stained with an anti-ERK antiserum. (B) The cAMP-induced increase in Raf-1 serine 259 phosphorylation is followed by inhibition of ERK. COS-1 cells were transfected with a small amount (0.4 μg) of FLAG-tagged Raf-1 in order to facilitate the use of the phosphoserine 259-specific antibody. Growing cells were treated with 10 μM H-89 for 30 min followed by 40 μM forskolin plus 100 μM IBMX for the indicated time points (Fsk/IBMX). Cells were lysed, and FLAG-Raf-1 was immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibodies and stained with a phosphoserine 259-specific antibody (upper panel). The blots were stripped and subsequently stained with a FLAG antibody (lower panel). ERK phosphorylation (upper panel) and expression (lower panel) were examined by blotting whole-cell lysates. (C) RafS259-induced reporter gene expression is refractory to inhibition by cAMP. NIH 3T3 cells were cotransfected with a GAL4-Elk-1 transcription factor, a CAT reporter gene under the control of GAL-4 DNA binding sites and Raf-1 or RafS259D. Cells were treated as indicated, and CAT expression was measured 8 h posttreatment.