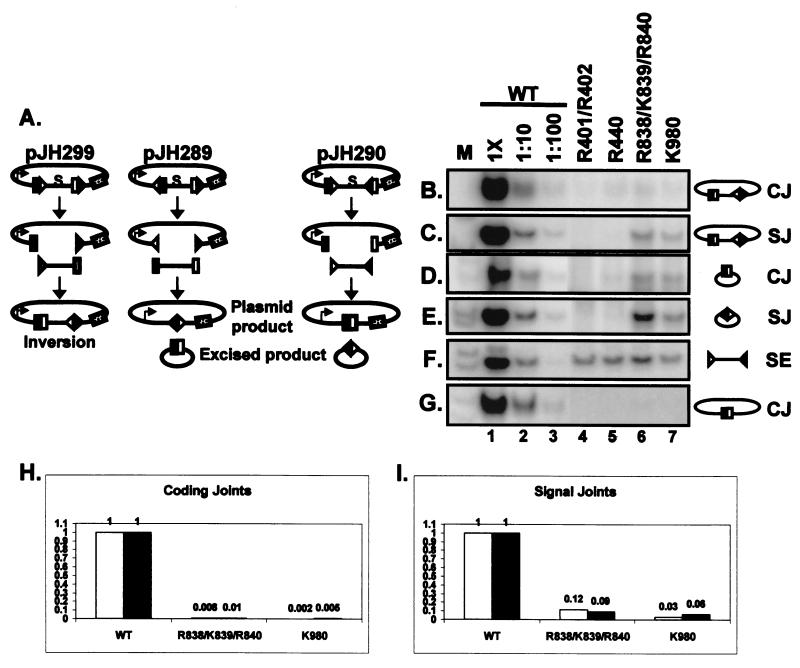
FIG. 6.
Identification of joining-deficient RAG-1 mutants. (A) Diagram illustrating the three recombination substrates used for in vivo analysis of the mutants. pJH299 assays for coding joints and signal joints formed by inversion on the plasmid. pJH289 assays for signal and coding joints formed by deletion, with the formation of signal joints on the plasmid product and coding joints on the excised product. pJH290 assays for coding joints and signal joints formed by deletion, with the formation of coding joints on the plasmid product and signal joints on the excised product. Coding flanks are represented by open and filled rectangles. The 12- and 23-RSS are indicated by open and filled triangles, respectively. The arrow on the plasmid products indicates the promoter for the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (cat) gene, represented by the stippled rectangle. cat is expressed upon recombination, removing the transcription terminator (represented by S). Joints formed on the plasmid products can be identified by a bacterial transformation assay (23). (B to G) PCR assays (24 cycles) to detect coding joints (CJ) (B, E, and G), signal joints (SJ) (C and E), and signal ends (SE) (F). Diagrams of the PCR substrates are shown on the right. Wild-type (WT)-transfected DNA was assayed at 1× and 1:10 and 1:100 dilutions. The mutants were assayed at 1× concentrations. M, radiolabeled markers. (B) PCR for inversional coding joints on pJH299. (C) PCR for inversional signal joints on pJH299. (D) PCR for coding joints on the excised product of pJH289. (E) PCR for signal joints on the excised product of pJH290. (F) Signal ends (12 RSS) from the pJH290 substrate were detected by ligation-mediated PCR. Analysis of signal ends from the pJH299 substrate gave similar results (data not shown). (G) PCR for coding joints on the plasmid product of pJH290. (H and I) Analysis of coding joints on the plasmid product of pJH290 (H) and signal joints on the plasmid product of pJH289 (I) by a transformation assay. The wild-type result is normalized to 1, and recombination by the mutants is shown relative to that of the wild type. Data from two independent experiments are shown (white and black bars).