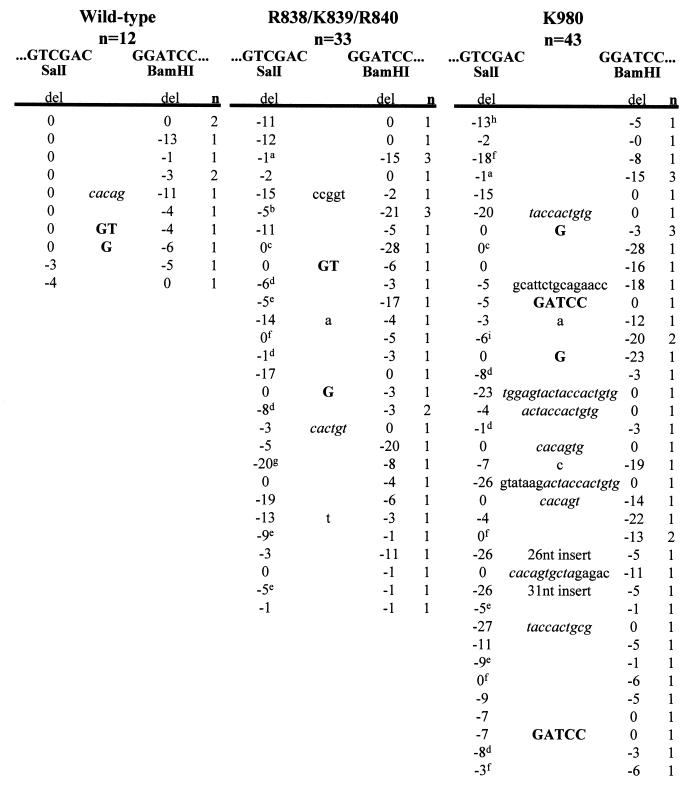
FIG. 7.
Nucleotide sequence analysis of coding joints from R838/K839/R840 and K980. PCR products containing coding joints were cloned and sequenced. The total numbers of unique sequences obtained for the wild type, R838/K839/R840, and K980 are indicated. The first 6 nt on either side of a perfect junction are shown. A perfect coding joint is GGTCGTTGATCCCCCATCGATGAGAGTCGAC-GGATCCTCTCATCGATGAGAGGATCGACGACGACATGGC. n, number of unique junctions with the indicated sequence. The number of deleted (del) nucleotides from each end is indicated beneath the corresponding end sequences. Letters in boldface type between the two ends indicate presumptive P nucleotides. Lowercase letters between the two ends indicate nucleotide insertions. Italics denote nucleotides derived from imprecise cleavage events. The sequence of the 26-nt insert is CTAGAGTCGATCCGTCCCCGGGCGAG. The sequence of the 31-nt insert is CAAAACCCTCTGTAACTCTAGATCCAGGAAT. Superscripts designate junctions that exhibit short sequence homologies, as follows: a, TCGA; b, CATCGATGAGAG; c, TCGAC; d, GA; e, G; f, C; g, TC; h, ATC; I, CATCGATGAGA.