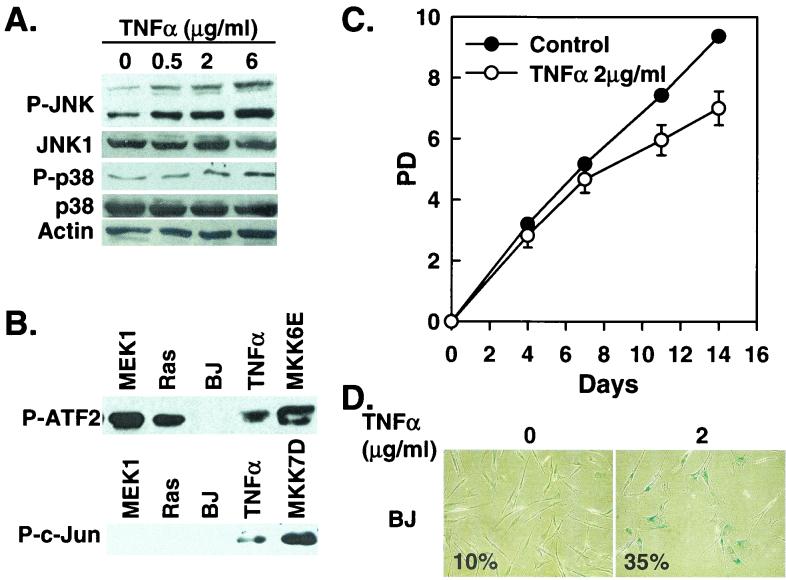
FIG. 4.
TNF-α induces senescence in BJ cells. (A) Western blot analysis of BJ cells (PD 24) treated with the indicated concentrations of TNF-α, showing levels of phospho-JNK (P-JNK), JNK1, phospho-p38 (P-p38), p38, and actin. (B) p38 (P-ATF2) and JNK (P-c-Jun) kinase activities were determined in BJ cells 8 days after being transduced at PD 32 with MEK1Q56P (MEK1), Ha-RasV12 (Ras), a vector control (BP), or MKK6E or after being treated with 2 μg of TNF-α/ml. p38 and JNK were isolated and assayed from 200 μg (p38) or 250 μg (JNK) of cell lysates by using the p38 MAP Kinase Assay Kit and the SAPK/JNK MAP Kinase Assay Kit (Cell Signaling), respectively. The phosphorylated substrates, ATF2 for p38 and c-Jun for JNK, were visualized by Western blot analysis by using antibodies against phospho-ATF2 or phospho-c-Jun. (C) PD of BJ cells (PD 29) treated with 2 μg of TNF-α/ml or vehicle control. Values are means ± standard deviations for triplicates. (D) Morphology of BJ cells treated with 2 μg of TNF-α/ml (2) or vehicle control (0), after staining for SA-β-gal (pH 6.0) at day 11 of the treatment. Numbers represent percentages of cells positive for SA-β-gal in each population.