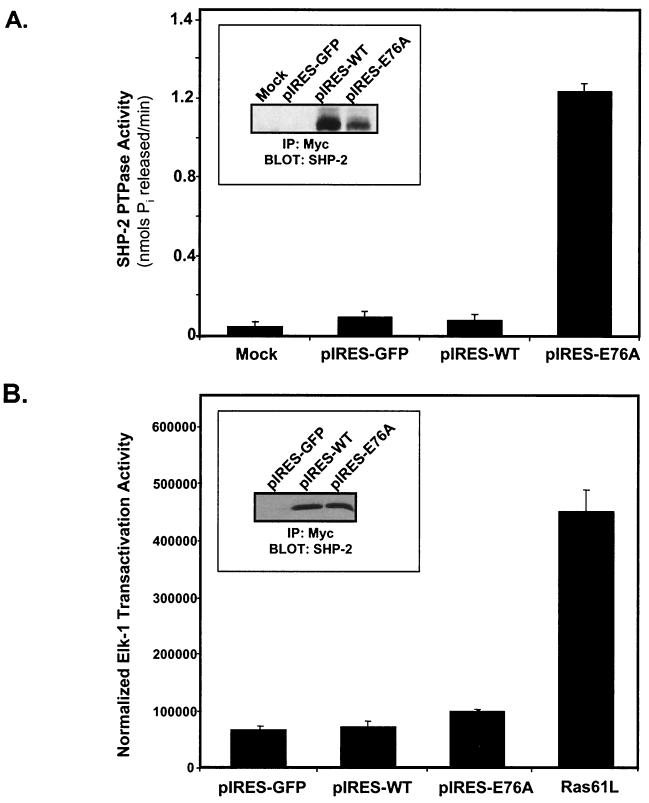
FIG. 7.
Effect of the constitutively active SHP-2 mutant on Elk-1 transactivation. (A) Myc-tagged WT SHP-2 and SHP-2 E76A were subcloned into the pIRES-GFP vector and were transfected, along with the pIRES-GFP control, into 293 cells. Anti-Myc-SHP-2 immune complexes were measured for phosphatase activity as described in Materials and Methods. Results shown are representative of two independent experiments, where E76A gives an ∼15-fold-higher level of pNPP hydrolysis than WT SHP-2. (Inset) Levels of SHP-2 protein assayed for phosphatase activity in these immune complexes were determined by immunoblotting of the resolved immune complexes with anti-SHP-2 antibodies. (B) C2C12 myoblasts were transfected with either pIRES-GFP, WT SHP-2 (pIRES-WT), or the constitutively active mutant of SHP-2 (pIRES-E76A). As a positive control, activated Ras [Ras61(Leu)] was also transfected into C2C12 myoblasts. After 24 h, the cultures were transferred to serum-free medium for a further 24 h, after which Elk-1 luciferase and β-galactosidase activities were determined. The experiments were performed in triplicate, and results are means ± standard errors of the means from three separate experiments, with Elk-1 luciferase activity normalized to β-galactosidase activity. (Inset) Equivalent expression levels of WT SHP-2 and SHP-2 E76A were confirmed following transfection of C2C12 myoblasts with pIRES-GFP, pIRES-WT, or pIRES-E76A. Transfectants were cultured for 48 h, and lysates were prepared and immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc (9E10) antibodies. IP, immunoprecipitation.