Abstract
Schedules of intermittent brain-stimulation reinforcement have been shown to maintain performances when a reinforcement is defined as several response-produced, brief trains of stimulation. The present experiments show that the number of response-produced trains permitted per reinforcement is a variable analogous to amount or magnitude of reinforcement in the conventional food-reinforcement experiment. Systematic effects were obtained when that variable was manipulated within a multiple schedule and also on variable-interval schedules programmed concurrently.
Full text
PDF


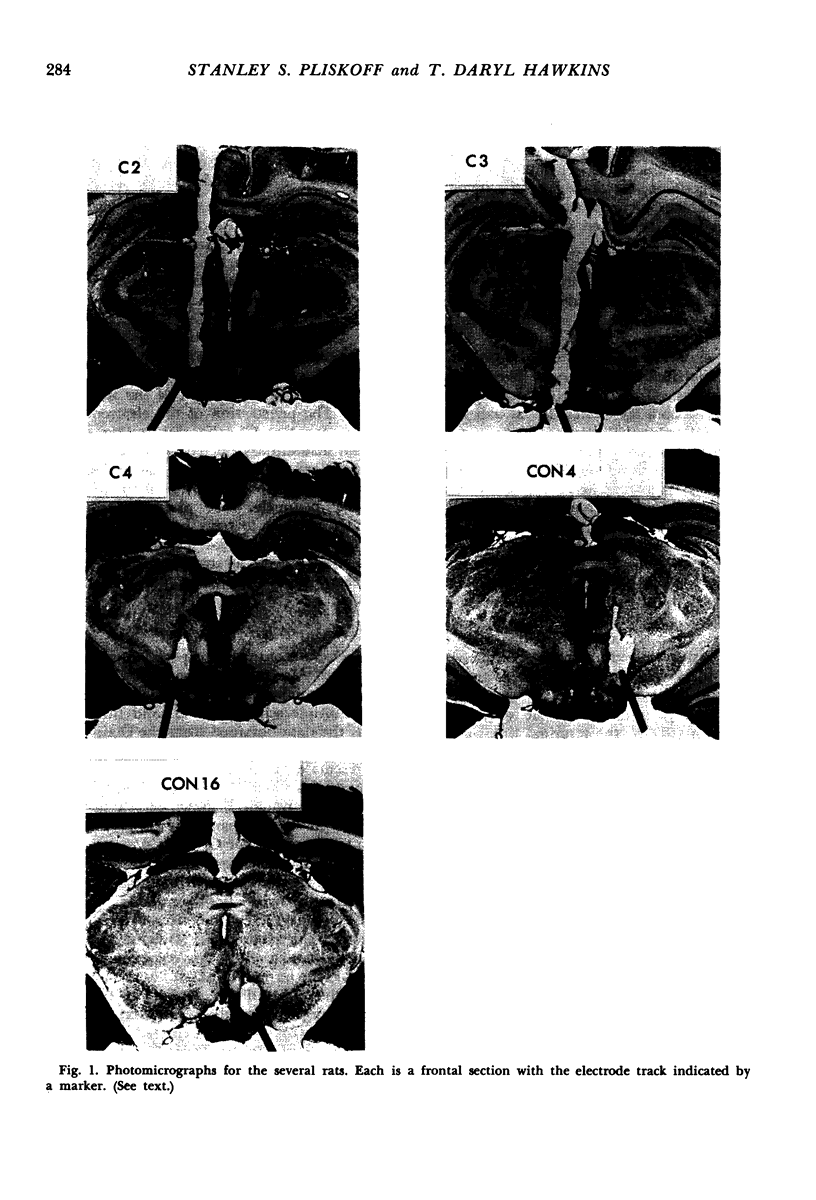
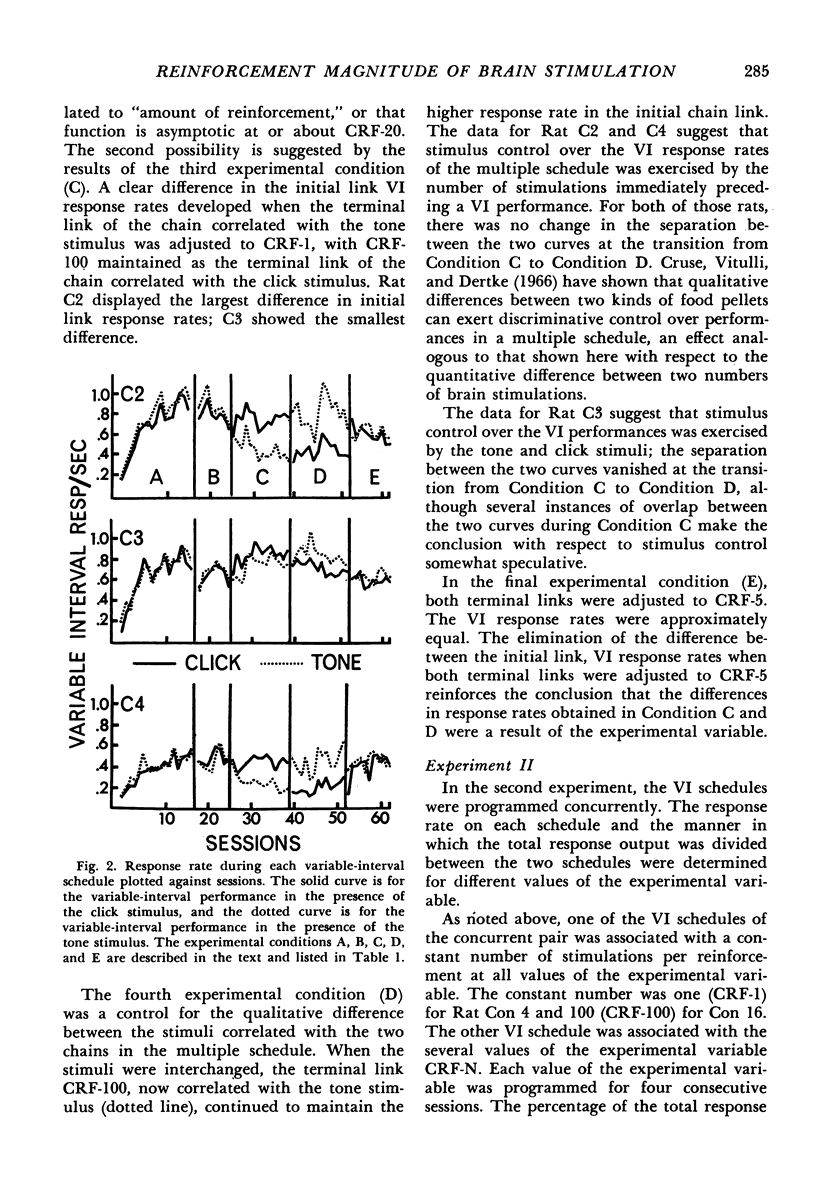
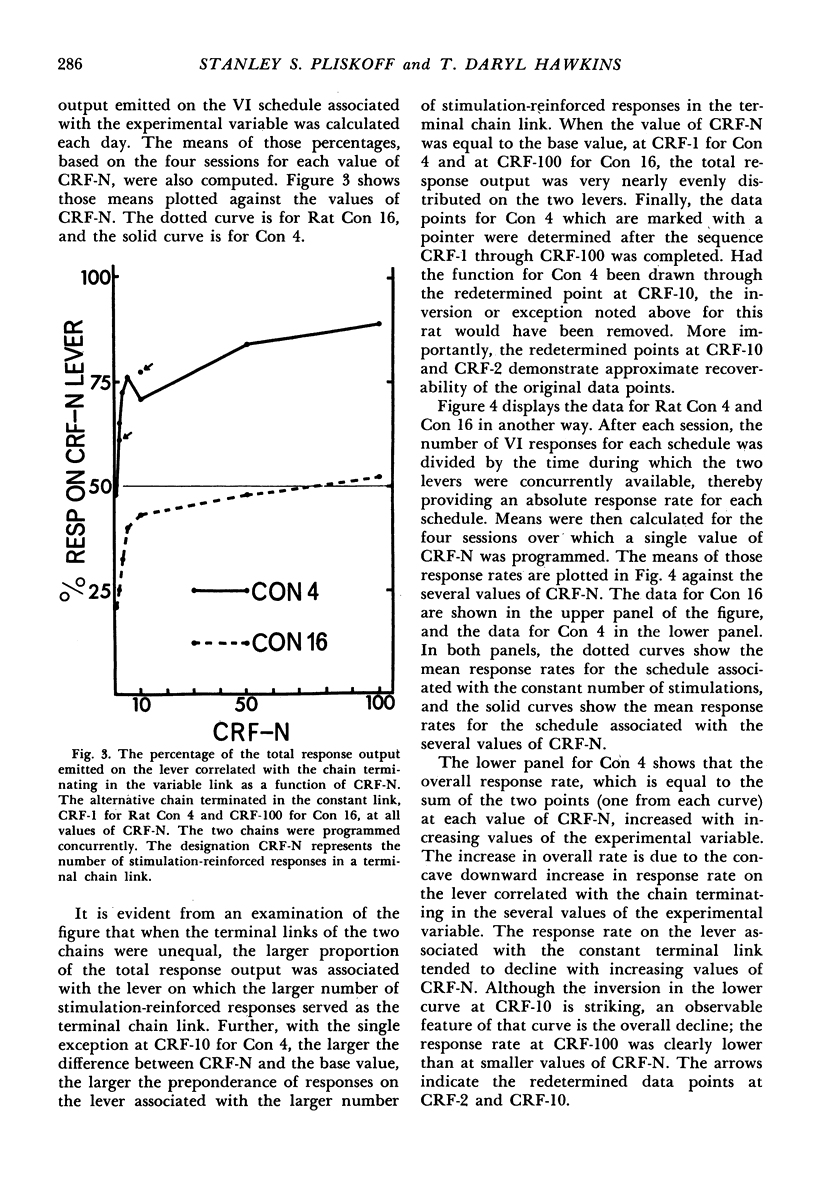
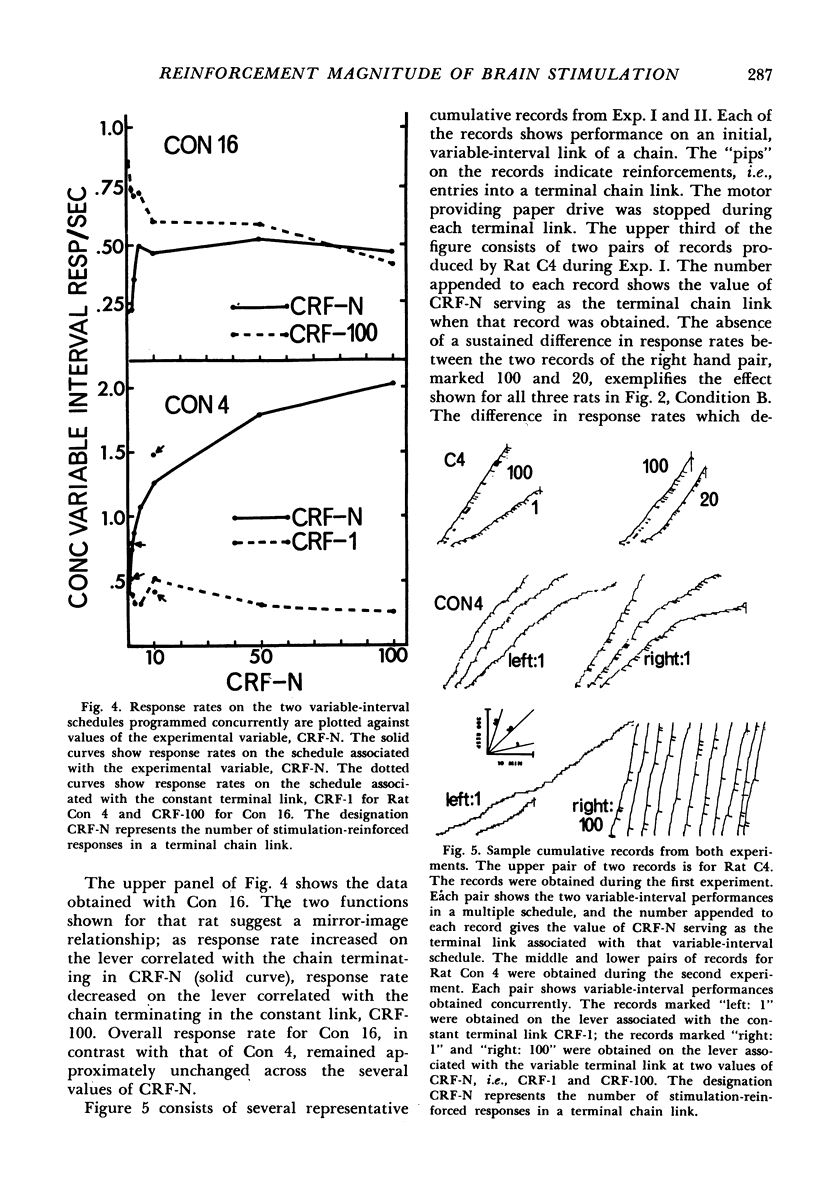


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOWER G. H., MILLER N. E. Rewarding and punishing effects from stimulating the same place in the rat's brain. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1958 Dec;51(6):669–674. doi: 10.1037/h0038925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATANIA A. C. Concurrent performances: a baseline for the study of reinforcement magnitude. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:299–300. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruse D. B., Vitulli W., Dertke M. Discriminative and reinforcing properties of two types of food pellets. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 May;9(3):293–303. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAWKINS T. D., PLISKOFF S. S. BRAIN-STIMULATION INTENSITY, RATE OF SELF-STIMULATION, AND REINFORCEMENT STRENGTH: AN ANALYSIS THROUGH CHAINING. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Jul;7:285–288. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODOS W. MOTIVATIONAL PROPERTIES OF LONG DURATIONS OF REWARDING BRAIN STIMULATION. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1965 Apr;59:219–224. doi: 10.1037/h0021818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLISKOFF S. S., WRIGHT J. E., HAWKINS T. D. BRAIN STIMULATION AS A REINFORCER: INTERMITTENT SCHEDULES. J Exp Anal Behav. 1965 Mar;8:75–88. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1965.8-75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALENSTEIN E. S. PROBLEMS OF MEASUREMENT AND INTERPRETATION WITH REINFORCING BRAIN STIMULATION. Psychol Rev. 1964 Nov;71:415–437. doi: 10.1037/h0040694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]