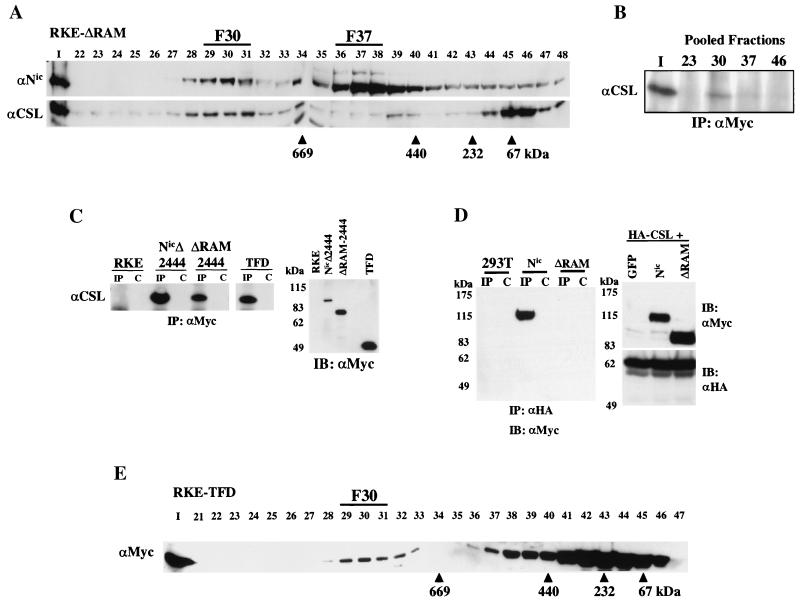
FIG. 2.
The RAM domain of Nic is dispensable for complex formation with CSL in RKE cells. (A) Nuclear lysate from ΔRAM-transformed RKE cells was fractionated by size exclusion chromatography. ΔRAM protein was visualized by Western blot analysis with bTAN15A (αNic). CSL protein was detected with anti-CSL antisera. (B) CSL stably integrates into the high-molecular-weight complex in the absence of the RAM domain. Fifty percent of the column load (I) and the three fractions encompassing the indicated gel filtration peaks were individually pooled and immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc antibody. CSL was detected with anti-CSL antisera. (C) CSL coimmunoprecipitates with the TFD of Nic. Whole-cell protein lysates from the indicated RKE cell lines were immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc antibody. CSL is found in the lanes precipitated with anti-Myc antibody (IP) but not in IgG control lanes (C). Expression of Nic derivative proteins was detected by Western blot analysis with anti-Myc antibody. Molecular mass markers are shown on the left. (D) The RAM domain is required for Nic and CSL interaction in 293T cells. 293T cells were cotransfected with the indicated expression plasmids. Whole-cell lysates were made and immunoprecipitated with the anti-HA antibody directed against CSL (lanes IP) or preimmune serum (lanes C); Nic proteins were detected by Western blot analysis with anti-Myc antibody. Five percent of each 293T lysate was separated by SDS-PAGE and processed for immunoblot analysis; proteins were detected with the indicated antibody (right). Molecular mass markers are shown on the left. (E) The TFD forms F30 in RKE cells. Cytoplasmic lysate from RKE cells expressing the TFD was fractionated by size exclusion chromatography, and the TFD was visualized by Western blot analysis with anti-Myc antibody.