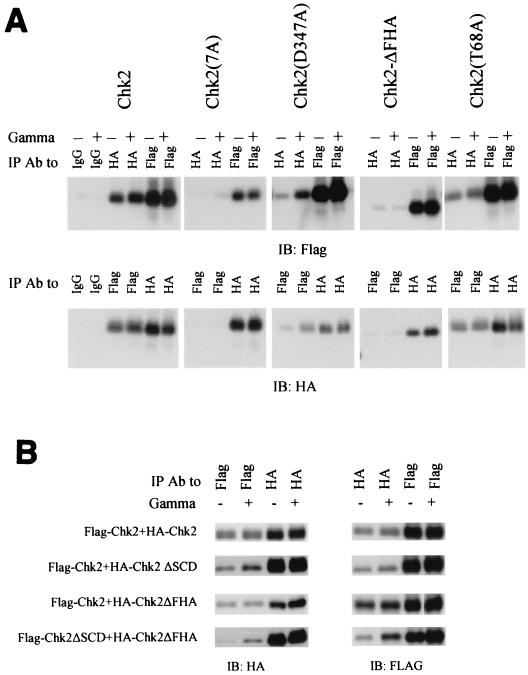
FIG. 7.
Chk2 oligomerization domains. (A) Requirements for oligomerization in 293 cells. HA-tagged and Flag-tagged versions of individual Chk2 mutants were expressed by transient transfection in 293 cells. Transfectants were exposed to 20 Gy of gamma irradiation 48 h after transfection. Cell lysates were harvested 2 h after irradiation, and equal amounts were used for immunoprecipitation with anti-HA antibody or anti-Flag antibody as indicated and immunoblotted with anti-Flag (top panel) or anti-HA (bottom panel). Because homologous immunoprecipitations (e.g., IP anti-Flag, blot anti-Flag) were more efficient than heterologous coimmunoprecipitations (e.g., IP anti-Flag, blot anti-HA), only a one-fifth equivalent of homologous immunoprecipitation samples was analyzed relative to the cross-immunoprecipitation samples. (B) Oligomerization of FHA domain and SCD in vivo. Performed as in A except that Flag-tagged and HA-tagged Chk2 molecules were evaluated in the pairwise combinations listed at left. (C) GST-FHA binds to activated Chk2. Various Chk2-GST fusion proteins expressed in bacteria were used to isolate HA-Chk2 stably expressed in 293 cells. Experiments were performed as described in the legend to A. Equal portions of lysate from nonirradiated and irradiated cells were incubated with GST-Chk2 or its mutants. Pulldowns were blotted for HA-Chk2 with anti-HA antibody and for input of GST fusion protein with anti-GST antibodies. Different sizes of GST fusions on the bottom panel were cropped and realigned from one autoradiograph. Total lysate used for anti-HA immunoprecipitation was one-fifth of that for the GST pulldown. (D) Bacterially produced FHA domain of Chk2 binds to SCD in HA-Chk2 and its mutants expressed in 293 cells after gamma irradiation. The strategy described for Fig. 6C was used. Only one representative immunoblot for input of GST fusions (bottom panel) is shown. Different sizes of GST fusions on the bottom panel were cropped from one autoradiograph. (E) T68 phosphorylation of Chk2 and its mutants in vivo. Cells were handled essentially as described in A. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA and detected by immunoblotting with anti-phospho-T68 or anti-HA. IP, immunoprecipitation; IB, immunoblotting; Ab, antibody.