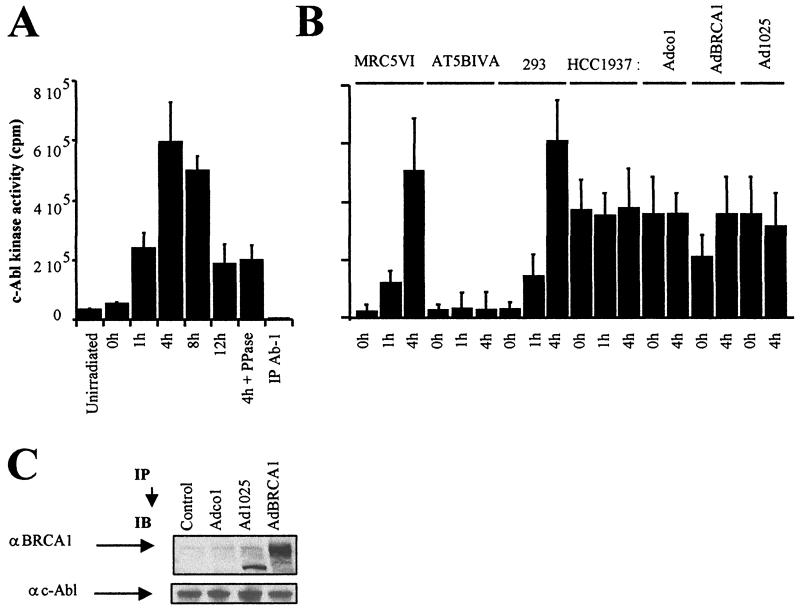
FIG. 5.
Tyrosine kinase activity of c-Abl after irradiation. (A) Tyrosine kinase activity of c-Abl measured from c-Abl immunoprecipitates (IP) of nuclear extracts from 293 cells exposed to 20 Gy and collected after irradiation at the indicated times. (B) Tyrosine kinase activity of c-Abl in nuclear extracts from 293, MRC5VI, AT5BIVA (ATM−/−), and HCC1937 (BRCA1-mutated) cells exposed to 20 Gy and incubated for the times indicated. HCC1937 cells were infected by empty cassette (Adco1), wild-type BRCA1 (AdBRCA1) adenoviruses, or adenoviruses expressing only the first 1,321 residues of BRCA1 (Ad1025). All the data presented are the mean plus standard error of triplicate experiments. The assay was controlled, with each sample using an anti-c-Abl (Ab-1) antibody that inhibits kinase activity, as recommended by the manufacturers (see Materials and Methods). We verified that the levels of c-Abl protein immunoprecipitated in all samples were similar (data not shown). (C) As a control for adenovirus expression, nuclear extracts from exponentially growing adenovirus-infected HCC1937 cells were subjected to immunoblotting (IB) using anti-BRCA1 (αBRCA1; MS110) and anti-c-Abl (αc-Abl; Ab-3) antibodies. It is noteworthy that the Ad1025 adenovirus produces a 156-kDa truncated BRCA1 protein.