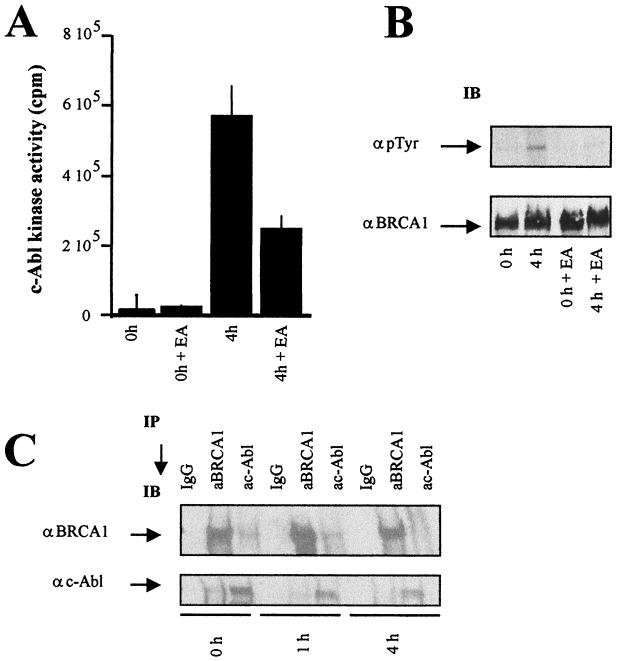
FIG. 7.
Effect of c-Abl kinase inhibition on the BRCA1-c-Abl complex. (A) c-Abl tyrosine kinase activity measured following c-Abl immunoprecipitation of nuclear extracts from untreated and EA-treated 293 cells exposed to 20 Gy and collected at the indicated times postirradiation. The error bars indicate standard deviations. (B) Nuclear extracts from irradiated control or EA-treated 293 cells were subjected to p-Tyr and BRCA1 immunoblotting (IB). α p Tyr, anti-p-Tyr; αBRCA1, anti-BRCA1. (C) Nuclear extracts from control and EA-treated cells were subjected to BRCA1 and c-Abl immunoprecipitation (IP) for BRCA1-c-Abl interaction using MS110 and Ab-3 antibodies, respectively. Preimmune mouse IgGs were used as controls. αc-Abl, anti-c-Abl. The experiments shown in panels B and C were carried out using 4% polyacrylamide gels in contrast to the experiment shown in Fig. 3A, where higher-percentage polyacrylamide gels were used. The difference in mobility shift postirradiation is therefore less pronounced in panels B and C.