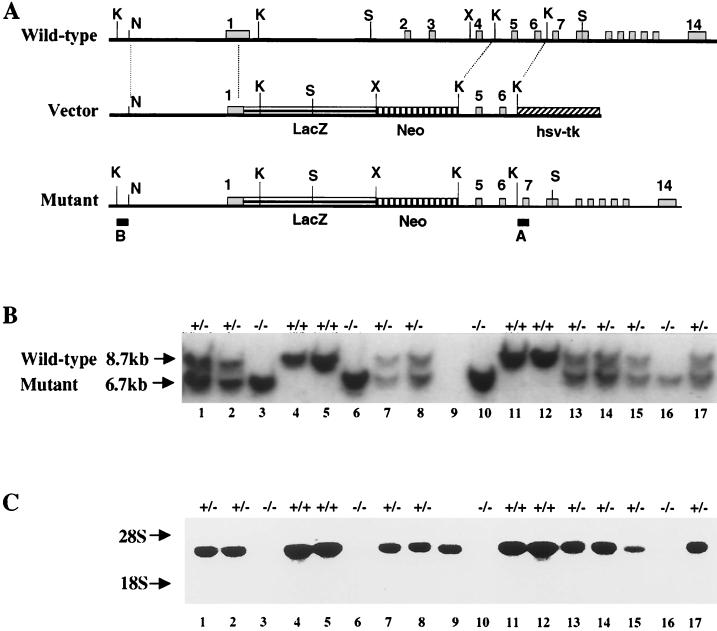
FIG. 1.
Schematic representation of the murine M-cadherin locus and design of the recombination vector. (A) The gene contains 14 exons. The recombination vector was constructed using a 4.6-kb NruI/KpnI fragment from the 5′ end of the gene and a 1.8-kb KpnI fragment encompassing exons 5 and 6 as the left and right recombination arms, respectively. The nls-lacZ gene and the PGK-neomycin resistance cassette were fused directly to the start codon in exon 1. The herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase (hsv-tk) gene was added downstream of the right recombination arm. Homologous recombination results in deletion of the coding region of exons 1 through 4 encoding the signal peptide and most of EC1. Hybridization probes A and B were used to identify wild-type and mutant alleles, respectively. (B) Typical Southern blot from two litters obtained by crossing heterozygous parents. DNA was digested with SacI restriction endonuclease and hybridized with probe A. Wild-type and mutant alleles are indicated by 8.7- and 6.7-kb fragments, respectively. The DNA sample in lane 9 was lost, and therefore no genotype is indicated for this mouse. (C) Northern blot using muscle RNA from the same animals shown in panel B hybridized with the EcoRV-SpeI 3′ fragment of M-cadherin cDNA (nucleotides 1271 to 2375). Mcad mRNA level is reduced in heterozygous and absent in homozygous mutant animals. Restriction sites: K, KpnI; N, NruI; X, XhoI; S, SacI.