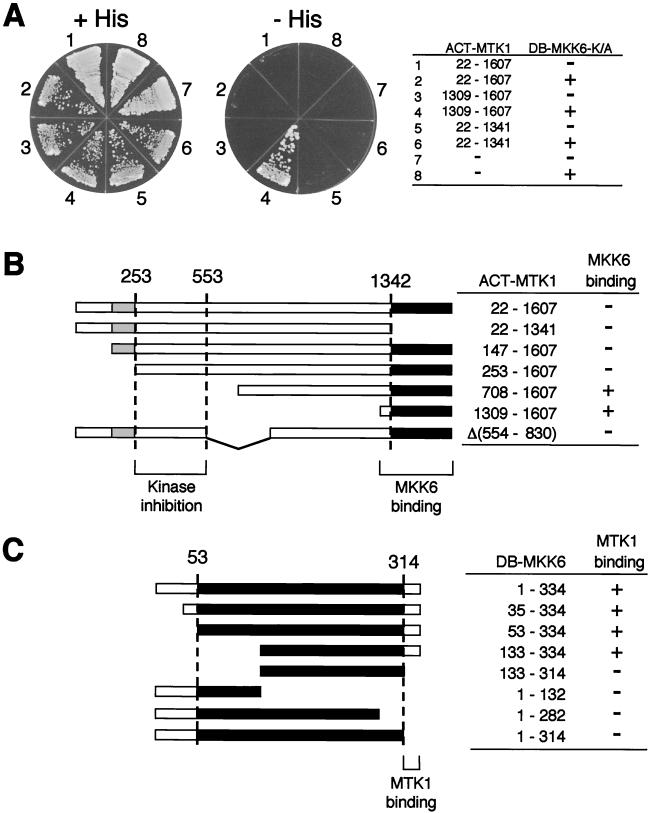
FIG. 3.
Two-hybrid interaction analysis between MTK1 and MKK6. (A) Interaction of various MTK1 segments fused to the GAL4 activation domain (ACT-MTK1 constructs) with MKK6-K/A fused to the LexA DB (DB-MKK6-K/A) was tested. Vectors used in these experiments were pACTII and pBTM118. Segments of MTK1 included in the ACT-MTK1 constructs are indicated. A minus sign in the ACT-MTK1 column indicates the vector without an insert. Yeast L40 cells were transformed with two plasmids (ACT-MTK1 and DB-MKK6-K/A constructs) as indicated. −, vector without an insert; +, vector with an insert. Transformed L40 cells were spread on the appropriate synthetic agar plates supplemented with (+His) or without (−His) histidine. A kinase-defective MKK6-K/A mutant was used to reduce the toxic effect of MTK1 expression. MTK1(1309-1607) encodes the kinase catalytic domain, whereas MTK1(22-1341) encodes the N-terminal noncatalytic domain. In situ β-Gal assays gave essentially identical results (not shown). (B) Summary of the experiments in panel A and additional two-hybrid tests. The MTK1 coding sequence is represented by the horizontal bar. Gray and filled boxes are the GADD45-binding domain and the kinase catalytic domain, respectively. The segment between amino acid positions 253 and 553 is required for autoinhibition of the MTK1-MKK6 interaction. +, growth on −His plates; −, no growth on −His plates. (C) Summary of two-hybrid analyses for the MTK1 binding site in MKK6. Binding of full-length (positions 1 to 334) and various deletion constructs of DB-MKK6-K/A was tested with ACT-MTK1(1309-1607) as a bait. The MKK6 coding sequence is represented by the horizontal bar. Filled boxes represent the kinase catalytic domain. The C-terminal noncatalytic region of MKK6 is necessary to interact with the MTK1 kinase domain. +, growth on −His plates; −, no growth on −His plates.