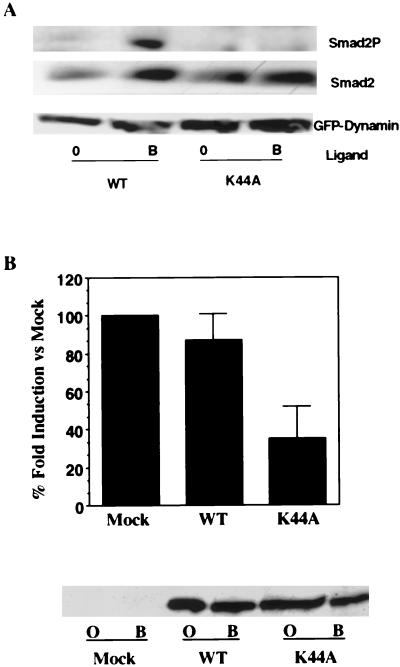
FIG. 4.
Dominant-negative dynamin 2ab inhibits Smad2 phosphorylation and TGF-β transcriptional activity. (A) Effect of dominant-negative dynamin 2ab on TGF-β-stimulated Smad2 phosphorylation. R1B cells (an Mv1Lu clone lacking the type I TGF-βR) were transiently transfected with the type I TGF-βR and GFP-tagged wild type or mutant (K44A) dynamin 2ab. Cultures were left untreated (lanes 0) or stimulated with 10 ng of TGF-β/ml for 1 h at 37°C. After normalization for transfection efficiency, equivalent protein (500 μg) was probed with a phospho-specific Smad2 antibody (Smad2P), Smad2 antibody (Smad2), or GFP antibody (GFP-Dynamin). (B) Dynamin regulates TGF-β-stimulated 3TP-Lux transcription. R1B cells were cotransfected with HA-tagged native type I receptor, 3TP-Lux, cytomegalovirus-β-galactosidase, and either pCMV5 vector (mock) DNA or GFP-tagged wild-type (WT) or dominant-negative K44A mutant dynamin 2ab isoforms. Cells were left untreated or were stimulated with 10 ng of TGF-β/ml for 24 h. The fold ligand induction in vector (mock)-transfected cells was assigned a value of 100%, and the effect of wild-type or K44A dynamin 2ab transfection is shown as the percentage of mock induction and represents the mean ± the SEM of two separate experiments performed in duplicate. In the lower panel, parallel lysates were immunoblotted with a GFP antibody to confirm the expression of transfected GFP-tagged wild type (WT) or dominant-negative dynamin 2ab (K44A) in untreated (lanes O) or TGF-β-stimulated (lanes B) cultures.