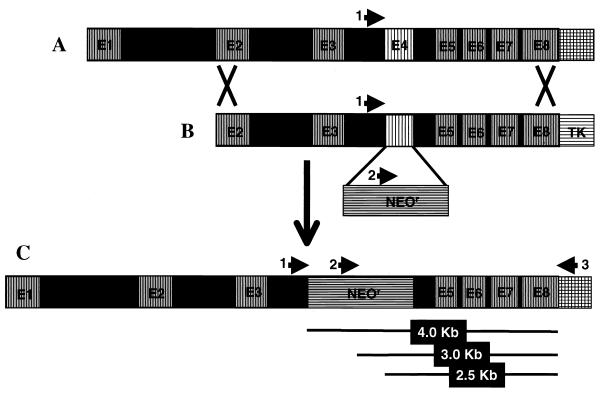
FIG. 1.
Schematic diagram of the AI gene-targeting event. (A) The genomic structure of mouse arginase I (AI) with eight exons and seven introns. (B) The AI gene-replacement vector, containing AI genomic sequences from exon 2 (E2) to exon 8 (E8): exon 4 (E4) is replaced by the neomycin resistance (NeoR) gene, and the HSV-tk (TK) gene provides strong selection against nonhomologous intergration events. (C) The product of homologous recombination of the AI gene-replacement vector into the mouse genome. The arrows represent the locations of primers used for genotyping the resultant ES cells and mice. 1, primer MAIF/I3; 2, primer NeoF(412); 3, primer MAIR3′UTR(∗+59). PCR A contains primers 1 and 2, and reaction B contains primers 2 and 3. The lines below segment C show the approximate sizes of the different products obtained. See Fig. 2 for an example of results obtained from wild-type, heterozygous, and AI-deficient mice.