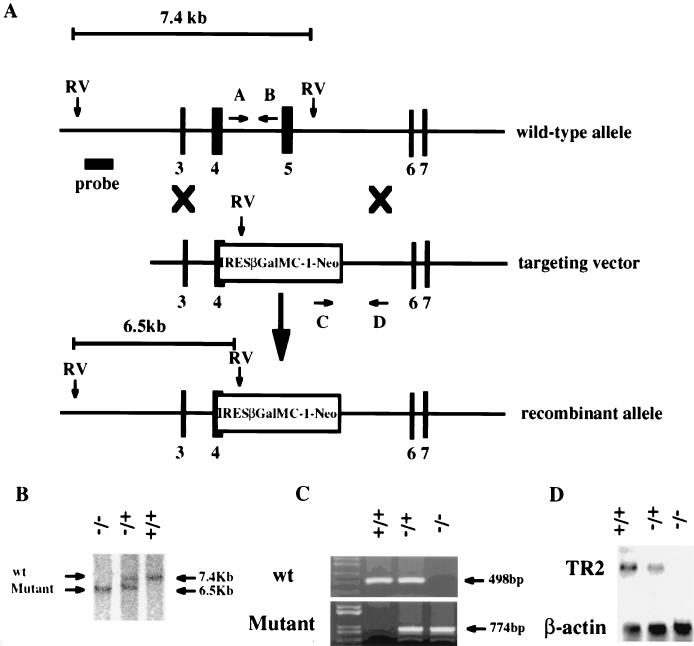
FIG. 1.
Targeted disruption of the murine TR2 gene. (A) Structure of wild-type allele, targeting construct, and recombinant locus. Black boxes represent exons of TR2. The expected fragments after EcoRV digestion are 7.4 kb for the wild-type allele and 6.5 kb for the mutant allele. Arrows indicate the primers used for PCR genotyping, and the bar represents the region used for probe. RV, EcoRV. (B) Southern blot analysis of mouse tail DNA isolated from the progeny of a mating between heterozygous parents. DNA was digested with EcoRV and hybridized with the probe indicated. (C) PCR analysis of mouse genomic DNA. The wild-type and targeted alleles give 498- and 774-bp PCR products, respectively. (D) Northern blot analysis of total RNA isolated from testis tissue from 6-week-old mice. The same membrane was sequentially hybridized with 32P-labeled TR2 and β-actin cDNA probes. +/+, wild-type mouse; +/−, heterozygous mutant mouse; −/−, homozygous mutant mouse; wt, wild type.