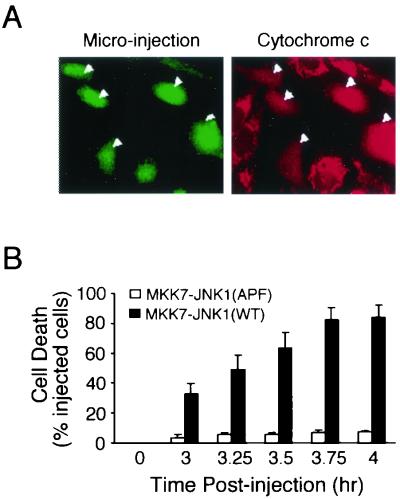
FIG. 7.
JNK causes rapid release of cytochrome c and apoptosis. (A) Activated JNK causes cytochrome c release from the mitochondria. CHO cells were microinjected with the MKK7-JNK1 expression plasmid together with dog IgG. The injected cells were visualized by staining with fluorescein-conjugated anti-dog IgG (green, indicated by arrowheads) and cytochrome c was stained with mouse anti-cytochrome c and rhodamine-conjugated goat anti-mouse antibodies. Cells releasing cytochrome c showed diffuse cytoplasmic and nuclear staining (red). Punctate mitochondrial staining was observed in the noninjected cells. (B) Time course of apoptosis induced by microinjection of MKK7-JNK1. CHO cells were microinjected with the indicated plasmids and apoptosis was evaluated by membrane blebbing and cell detachment. The data presented represent the means ± SD of data obtained for four independent experiments.