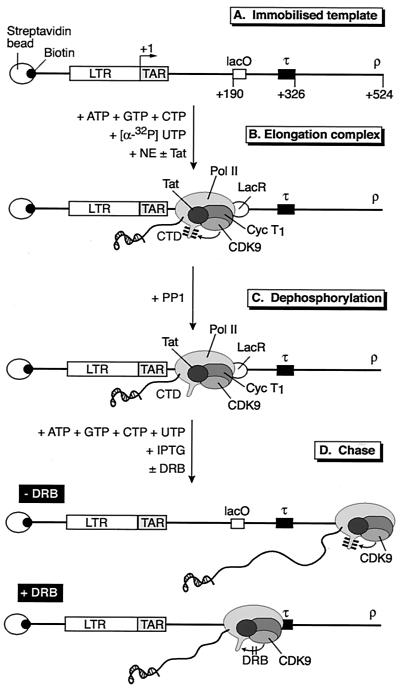
FIG. 1.
Strategy used for analyzing transcription elongation complexes. (A) Structure of HIV-LTR template. DNA templates containing the lac operator (lacO) binding site for the lac repressor protein (LacR) and a terminator (τ) sequence were biotinylated and bound to streptavidin beads. (B) Elongation complexes were trapped by the lac repressor (LacR) after incubation of the immobilized templates with HeLa nuclear extract (NE) in the presence of nucleotide triphosphates and LacR and in the absence or presence of Tat. The CTD of the RNA polymerase was phosphorylated during the elongation reaction due to the activity of CDK7 and CDK9. (C) Elongation complexes arrested by LacR were treated with PP1 to remove phosphate groups from the CTD. (D) The phosphatase-treated complexes can resume transcription elongation after the addition of nucleotides and IPTG. During the chase reaction the CTD became phosphorylated by CDK9. The addition of DRB blocked the rephosphorylation of the CTD and induced pausing of the transcription complex at the terminator sequences.