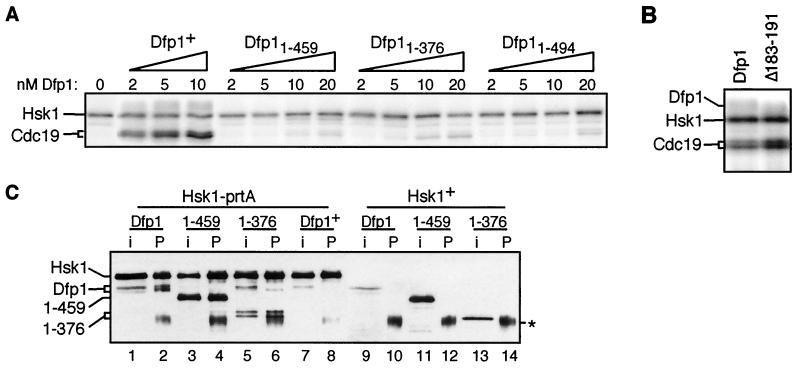
FIG. 6.
(A) dfp1 motif C mutants are poor Hsk1 activators in vitro. Cdc19 kinase assays were performed by incubating 5 nM Hsk1 with the indicated amounts of purified Dfp1, Dfp11-459, Dfp11-376, and Dfp11-494 protein in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP. Reaction products were fractionated by SDS-PAGE and exposed to a PhosphorImager screen. The positions of Hsk1 and Cdc19 are indicated. (B) A motif N mutant Dfp1 is an efficient activator of Hsk1 in vitro. Cdc19 kinase assays were performed with 5 nM Hsk1 and 5 nM Dfp1 or Dfp1Δ183-191. Reaction products were fractionated by SDS-PAGE and exposed to a PhosphorImager screen. (C) Dfp1 motif C mutants bind to Hsk1. Extracts were prepared from strains expressing protein A-tagged Hsk1 (lanes 1 to 8) and untagged Hsk1 (lanes 9 to 14). Extracts were incubated with IgG-agarose, and precipitates were fractionated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose. Hsk1 and Dfp1 were detected with the anti-HA epitope antibody 16B12. For each strain, a sample equivalent to half of the input extract (i) was fractionated alongside the entire immunoprecipitate (P). Strains coexpressed the following proteins: lanes 1 and 2, Hsk1-prtA and Dfp1-3HA (JOY7); lanes 3 and 4, Hsk1-prtA and Dfp11-459-3HA (JOY8); lanes 5 and 6, Hsk1-prtA and Dfp11-376-3HA (JOY9); lanes 7 and 8, Hsk1-prtA and untagged Dfp1 (JOY6); lanes 9 and 10, untagged Hsk1 and Dfp1-3HA (GBY572); lanes 11 and 12, Hsk1 and Dfp11-459-3HA (AFY6); lanes 13 and 14, Hsk1 and Dfp11-376-3HA (AFY7). The asterisk indicates IgG heavy chain. Dfp11-376 appears as a doublet in some experiments (lanes 5 and 6), likely due to proteolysis in vitro.