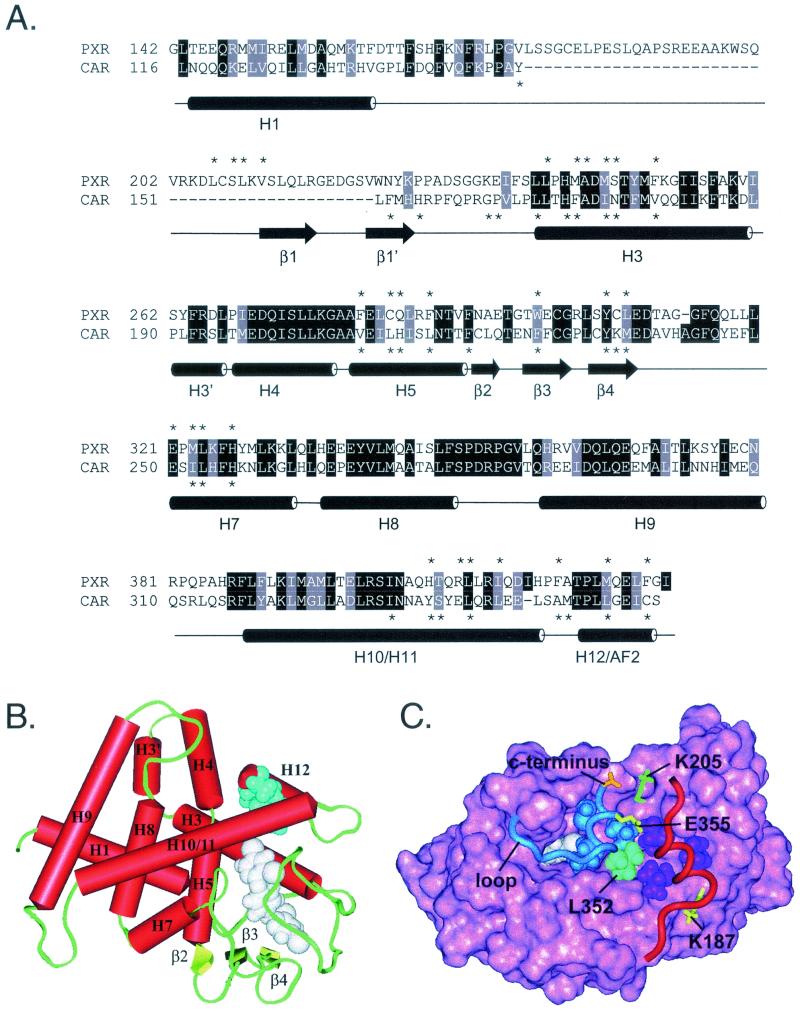
FIG. 4.
Homology model of the CAR ligand-binding domain. (A) Structure-based amino acid sequence alignment of human PXR and mouse CAR ligand-binding domains. Cylinders represent α-helices in PXR as defined in Protein Data Bank file 1ILH. Arrows represent β-strands. Specific α-helices (H) and β-strands (β) are identified by number. PXR lacks H2 and H6, which are found in most other LBDs. Identical residues are shown on a black background. Homologous residues are shaded gray. Asterisks indicate residues that line the internal ligand-binding cavity in the crystal structure of PXR or the model of CAR. Helices 10 and 11 are indicated as one continuous helix, as described in the PXR crystal structure (51). (B) Homology model of mouse CAR based on the crystal structure of human PXR. Specific structural elements are labeled. TCPOBOP (white) is shown in one of several possible conformations within the ligand-binding cavity, as described in Materials and Methods. Androstanol (blue) can mimic the hydrophobic side chains of H12 (L352, L353, I356, and C357). Thus, androstanol is shown superimposed on H12/AF2 and docked in the groove normally occupied by this helix when it assumes the active conformation (see Discussion). In this model, the residues that line the androstanol pocket are N175 (backbone oxygen only), T176, V179, Q180, K205, A208, V209, S337, Y338, L340, Q341, M349, and T350. (C) Top view of the mouse CAR homology model. Pink, solid rendering of mouse CAR LBD residues 116 to 344. Blue, ribbon rendering of residues 345 to 358, which constitute H12/AF2 and the loop that precedes it. L353, I356, and C357, residues that mimic the three leucines in the canonical LXXLL motif of CAR, are shown in blue space-filling representation. Cyan, L352, the residue that precedes the LXXLL motif and forms part of the hydrophobic cleft in which coactivator binds. Red, ribbon rendering of SRC-1 coactivator peptide. The three leucines of the SRC-1 RID2 LXXLL motif (690, 693, and 694) are shown in purple space-filling representation. Yellow, classical charge clamp residues. E355 neutralizes the positive dipole at the N terminus of the coactivator peptide, whereas K187 neutralizes the negative dipole at the C terminus. Orange, carboxylate group at C terminus of CAR. Green, K205, which forms a salt bridge with the C-terminal carboxylate to stabilize H12/AF2 in the active conformation. White, TCPOBOP docked in the ligand-binding cavity beneath H12. The loop between H11 and H12 is indicated and points to the junction between residues 345 and 346, the insertion site of three alanine residues.