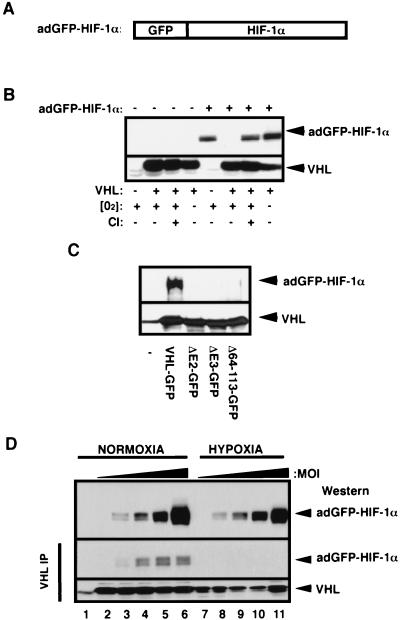
FIG. 1.
Characterization of the adGFP-HIF-1α fusion protein. (A) Schematic representation of HIF-1α fused to GFP. The cDNA encoding for the alpha subunit of the HIF-1α was fused to the C terminus of the cDNA of the GFP, resulting in GFP-HIF-1α fusion protein. (B) Proteolysis of adGFP-HIF-1α is proteasome mediated and VHL and oxygen dependent. VHL−/− RCC cells (cell line 786-0) or the VHL(+) WT-7 stable cell line (expressing HA-tagged VHL) were either not infected (−) or infected (+) with low titers (MOI) of the adGFP-HIF-1α. Cells were incubated in normal oxygen tension (O2+) or in hypoxic conditions (1% oxygen; O2−) for 4 h. Normoxic cells were also incubated in the presence (CI+) or the absence (CI−) of calpain inhibitor I for 2 h. Cell lysates were subjected to an SDS-8% PAGE analysis, and a Western blot was detected with anti-HIF-1α or anti-HA antibody. (C) The fusion protein adGFP-HIF-1α binds to VHL-GFP in vitro. Lysates of adGFP-HIF-1α infected VHL−/− RCC cells were incubated in reticulocyte lysates programmed with pcDNA vector alone (−), expressing FLAG tagged-VHL-GFP or mutants of the α or β domain (ΔE2-GFP, ΔE3-GFP, and Δ64-113-GFP). The resulting mixture was immunoprecipitated with M2 monoclonal antibody and immunoblotted with anti-HIF-1α or anti-M2 antibody. (D) adGFP-HIF-1α binds to VHL in normoxia but not in hypoxia. VHL-GFP stable cell lines were infected with increasing amounts of adGFP-HIF-1α virus and incubated in normoxia or hypoxia for 4 h. Immunoprecipitation was carried out in normoxic or hypoxic conditions with M2 antibody. Immunodetection of input (top panel) and of the immunoprecipitation was done with an anti-HIF-1α or anti-M2 antibody. Lane 1 represents M2 beads alone.