FIG. 3.
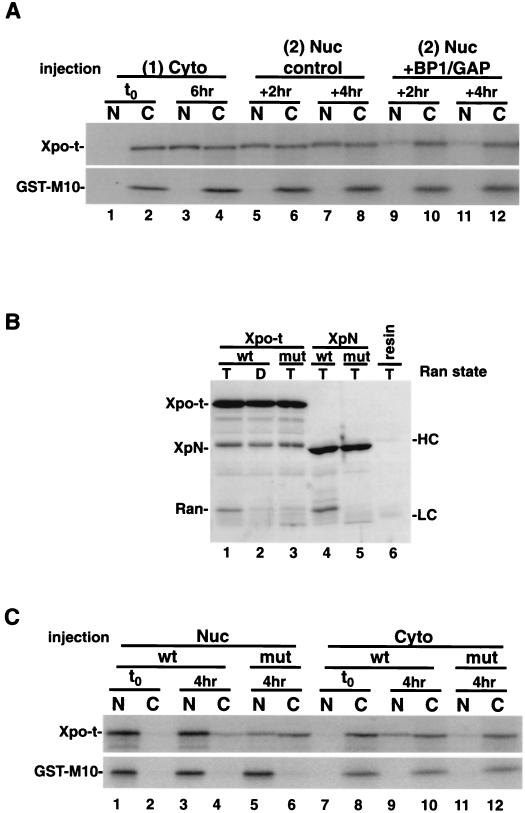
Xpo-t is predominantly a nuclear protein at steady state because it binds to RanGTP. (A) Depletion of nuclear RanGTP alters the steady-state localization of Xpo-t. 35S-labeled Xpo-t was injected into the oocyte cytoplasm (lanes 1 and 2) and incubated for 6 h to allow Xpo-t to equilibrate into the nucleus (lanes 3 and 4). At this time point a second injection into the nucleus was performed with a mixture containing either 1 μM RanGAP-10 μM RanBP1 and injection dye (lanes 9 to 12) or only injection dye (lanes 5 to 8). Oocytes were dissected after 2 or 4 h, and the samples were separated by SDS-12% PAGE and detected by autoradiography. (B) In vitro binding of RanGTP to wild-type or F54A/F55A mutant Xpo-t or XpN. Experimental conditions were as for Fig. 1A. (C) The RanGTP-binding Xpo-t mutant mislocalizes to the cytoplasm at steady state in Xenopus oocytes. 35S-labeled Xpo-t or the F54A/F55A mutant was injected into either the nucleus (Nuc) or cytoplasm (Cyto) of oocytes, the oocytes were incubated for 4 h and dissected, and samples were processed as described above. Cyto, cytoplasm; Nuc, nucleus; t0, time zero; N, nuclear fraction; C, cytoplasmic fraction; wt, wild type; mut, mutant; HC, IgG heavy chain; LC, IgG light chain.