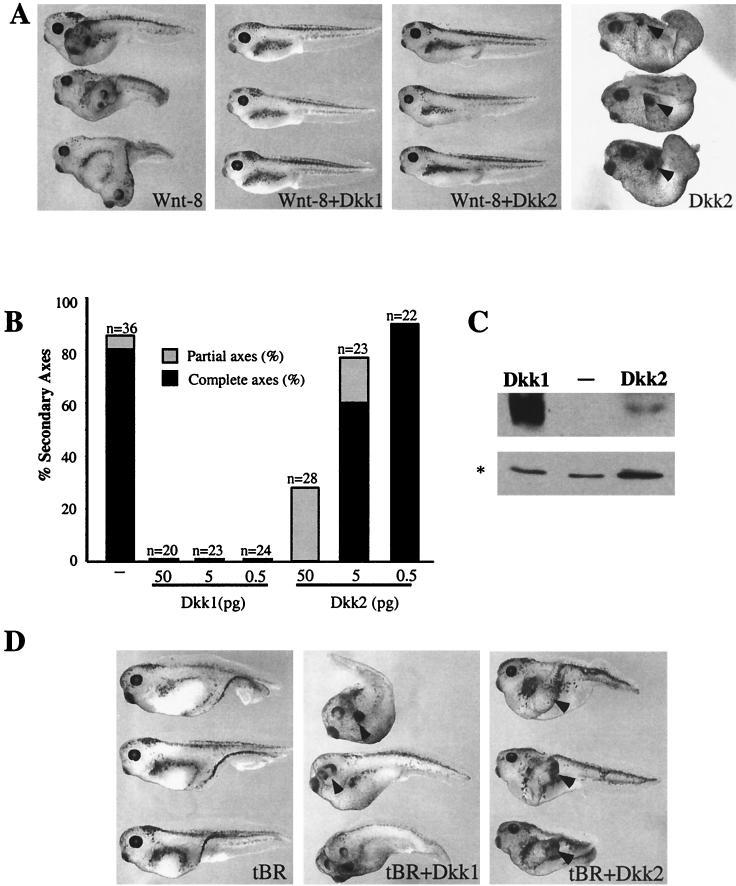
FIG. 1.
Dkk1 and Dkk2 inhibit Wnt8-dependent secondary axes and synergize with tBR in head induction. (A) Both Dkk1 and Dkk2 inhibit Wnt8-induced secondary axes. Embryos at the four- to eight-cell stage were injected into one ventro-vegetal blastomere with Wnt8 mRNA (1 pg) and Dkk1 (2.5 pg) or Dkk2 (50 pg) mRNAs. The dose of Dkk2 mRNA is higher than that of Dkk1 RNA to compensate for lower protein expression. (B) Dose-dependent inhibition of Wnt8 by Dkk1 and Dkk2. Embryos were injected as described above with Wnt8 mRNA (1 pg) and Dkk1 or Dkk2 mRNAs at the indicated doses. Results are representative of three separate experiments. Complete axes are defined by the presence of a second head with eyes; partial axes are composed of a secondary trunk without anterior head structures. (C) Expression levels of Flag-tagged Dkk1 and Dkk2 in Xenopus embryos. Each blastomere of four-cell embryos was injected with 5 ng of the indicated Dkk RNAs. Embryo lysates prepared at stage 9 were separated in SDS-12% polyacrylamide gels, transferred to Immobilon P membrane, and probed with anti-Flag M2 antibodies. A nonspecific protein band marked by an asterisk reflects loading. (D) Both Dkk1 and Dkk2 synergize with tBR to induce head structures. Embryos were injected with tBR mRNA (20 pg) and Dkk1 (2.5 pg) or Dkk2 (20 pg) mRNA, as indicated. Arrowheads indicate secondary head structures.