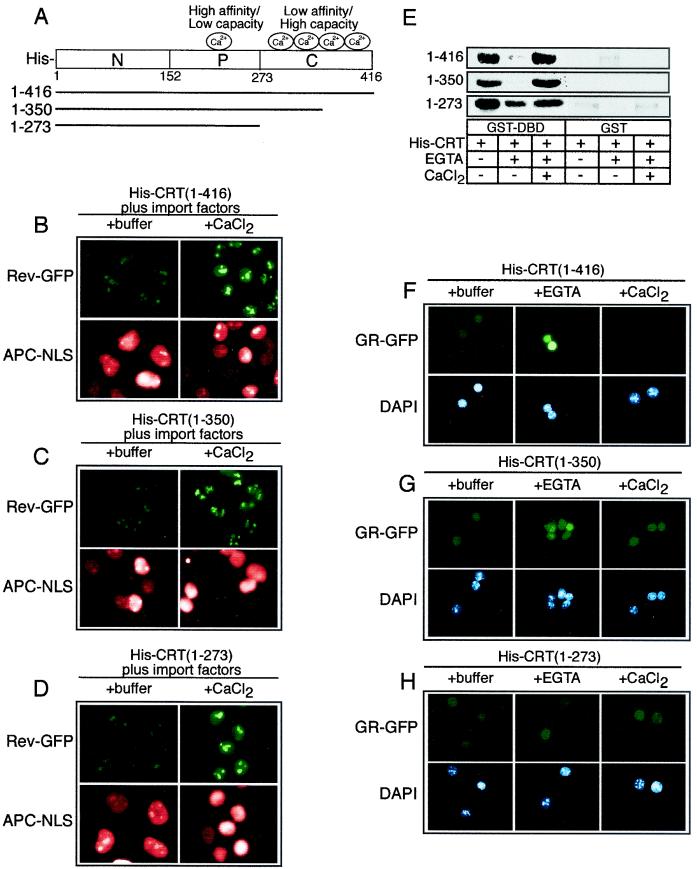
FIG. 6.
The low-affinity Ca2+ binding sites in the C-terminal domain of CRT are not essential for nuclear export activity. (A) Diagram of the CRT structure and sites of Ca2+ binding. (B to D) Export assays performed with CRT proteins containing deletions in the low-affinity Ca2+ binding C-terminal domain. CRT lacking the entire C-terminal domain retains its Ca2+-dependent inhibition of NES export, indicating that this is probably due to the high-affinity, low-capacity Ca2+ binding site. (E) EGTA-sensitive binding of CRT to the DBD is partially lost on removal of the C-terminal domain (residues 1 to 273). (F to H) Removal of the entire C-terminal domain (residues 1 to 273) from CRT abrogates the EGTA-sensitive export of GR. Although the C-terminal domain of CRT is not required for export, it is necessary for Ca2+ regulation of GR export.