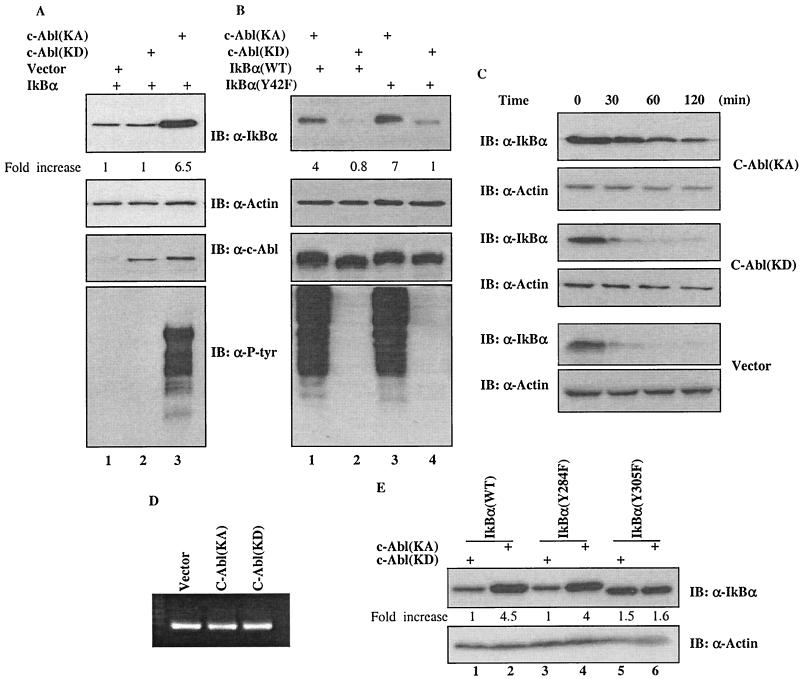
FIG. 2.
Upregulation of IκBα by c-Abl in a kinase-dependent manner. (A) A vector expressing IκBα was cotransfected with a plasmid encoding control vector (lane 1), c-Abl(KD) (lane 2) or c-Abl(KA) (lane 3) into 293T cells. Cell lysates prepared at 24 h after transfection were subjected to Western analysis using the indicated antibody. The densitometric intensity of the IκBα band was scanned and numbers represent fold increase over that of vector control that was set as 1. (B) A plasmid containing cDNA of wild type (lanes 1 and 2) or Y42F (lanes 3 and 4) mutant of IκBα was coexpressed with c-Abl(KA) (lanes 1 and 3) or c-Abl(KD) (lanes 2 and 4) in U2OS cells and the cells were analyzed as described for panel A. (C) Half-life of IκBα in the vector, c-Abl(KD)- or c-Abl(KA)-expressing cells was determined by monitoring the disappearance of IκBα after addition of cycloheximide (20 μg/ml). (D) mRNA was isolated and analyzed by RT-PCR using a kit according to the manufacturer's protocol (Promega). (E) A plasmid encoding wild-type IκBα (lanes 1 and 2), IκBα(Y284F) (lanes 3 and 4) or IκBα(Y305F) (lanes 5 and 6) was cotransfected with c-Abl(KA) (lanes 2, 4 and 6) or c-Abl(KD) (lanes 1, 3 and 5). Cellular abundance of IκBα was analyzed 24 h after transfection and actin was used as a loading control.