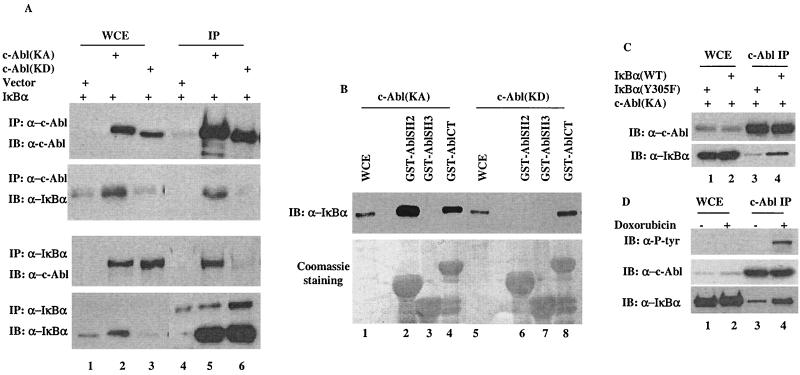
FIG. 3.
A phosphorylation-facilitated interaction between IκBα and c-Abl. (A) A vector expressing IκBα was coexpressed with a control vector, c-Abl(KA) or c-Abl(KD). Cell lysates prepared 24 h after transfection were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-c-Abl (top two panels) or anti-IκBα (lower two panels). Whole-cell extracts (lanes 1 to 3) or immunocomplexes (lanes 4 to 6) were analyzed by Western blotting using the indicated antibodies. (B) Cell lysates prepared from c-Abl(KA)- (lanes 1 to 4) or c-Abl(KD)- (lanes 5 to 8) expressing cells were incubated with the indicated GST-fusion proteins. The adsorbates were extensively washed, resolved on SDS-PAGE and either immunoblotted with anti-IκBα (top panel) or stained with Coomassie dye (bottom panel). Whole-cell extracts (WCE, lanes 1 and 5) were included as blotting controls. (C) A vector expressing wild-type IκBα (lanes 2 and 4) or IκBα (Y305F) mutant (lanes 1 and 3) was cotransfected with c-Abl(KA). Cell lysates prepared 24 h after transfection were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-c-Abl. Whole-cell extract (lanes 1 and 2) and c-Abl immunocomplexes (lanes 3 and 4) were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-c-Abl (top panel) or anti-P-Tyr (bottom panel). (D) U2OS cells treated with or without doxorubicin (2 μM for 12 h) were analyzed by anti-c-Abl immunoprecipitation followed by Western analysis using the indicated antibodies.