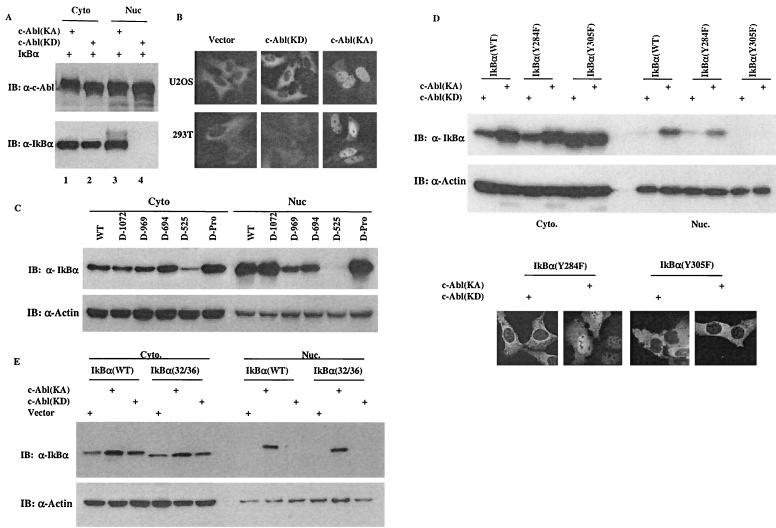
FIG. 5.
The c-Abl-induced IκBα nuclear accumulation contributes to its ability to upregulate the IκBα protein levels. (A) A vector containing cDNA of IκBα was cotransfected with a plasmid encoding c-Abl(KA) or c-Abl(KD). Cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions were prepared at 24 h posttransfection and subjected to Western analysis using anti-c-Abl (top panel) or anti-IκBα (bottom panel). (B) A plasmid encoding GFP-IκBα was cotransfected with a control vector, c-Abl(KD) or c-Abl(KA) into U2OS (top panels) or 293T cells (bottom panels). The cells were processed as described in Materials and Methods and examined under a fluorescence microscope. (C) An IκBα-expressing vector was cotransfected with plasmids encoding the indicated c-Abl deletion mutants. Cell fractions were prepared at 24 h posttransfection and analyzed by Western blotting using anti-IκBα (top panel) and anti-actin (bottom panel). (D) A plasmid encoding IκBα(wild type), (Y284F) or (Y305F) was cotransfected with c-Abl(KA) or c-Abl(KD). Cell fractions were prepared at 24 h after transfection and Western blotted with anti-IκBα or anti-actin. U2OS cells were transfected with the indicated vectors and analyzed as described for panel B. (E) Cell fractions were prepared from cells transfected with the indicated vectors and analyzed as described for panel C.