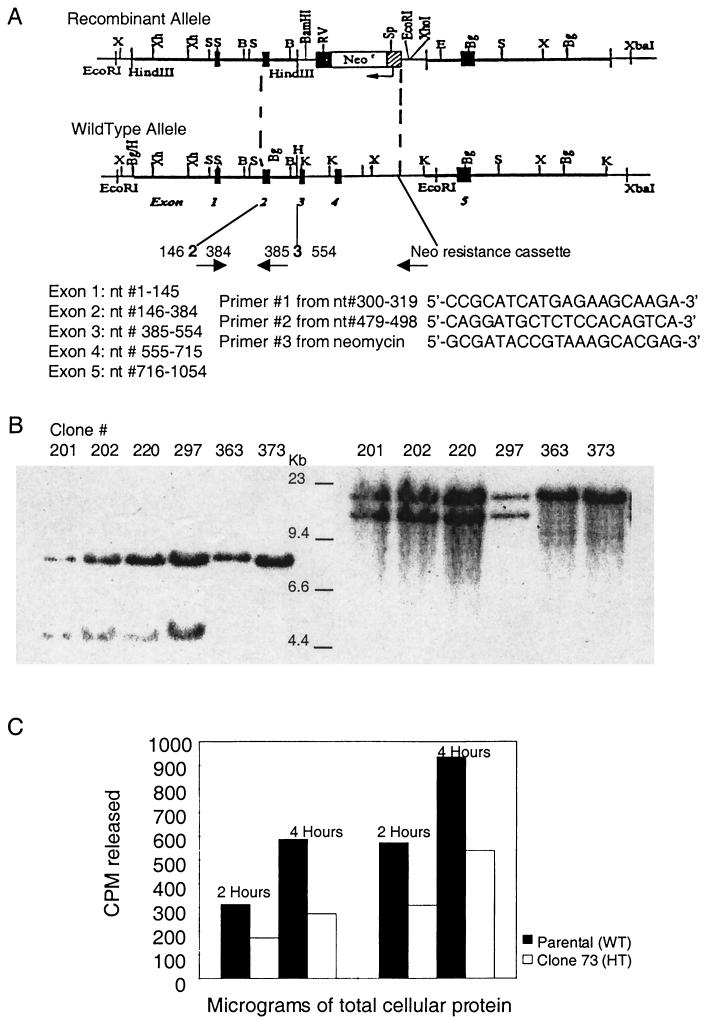
FIG. 1.
(A) Targeted disruption of mNth1. The mNth1 locus consists of five exons, as represented by the numbered black boxes in the schematic of the wild-type allele. To generate the recombinant allele, exons 2 through 4 were replaced with the neomycin resistance cassette via homologous recombination. The positions of the PCR primers used in routine genotyping are indicated by arrows, and their sequences are numbered based upon their location in the mNth1 cDNA. Abbreviations: B, BamHI; Bg, BglII; E, EcoRI; K, KpnI; RV, EcoRV; S, SacI; Sp, SpeI; X, XbaI;Xh, XhoI. (B) Southern blot analysis of ES cell clones. In the left panel, probing of the 5′ region after EcoRI and EcoRV digestion of genomic DNA yielded a 7.4-kb band for the wild-type allele and a 4.5-kb band for the recombinant allele, due to the insertion of a new EcoRV (RV) site in the targeting vector. In the right panel, probing of the 3′ region after SpeI digestion of genomic DNA produced an 18.0-kb band for the wild-type allele and a 14.4-kb band for the recombinant allele, due to the insertion of a new SpeI (Sp) site in the targeting vector. (C) mNth1 gene dosage effect in ES cells. The enzymatic activity of parental mNth1+/+ (wild type [WT]) and candidate heterozygous (HT) mNth1+/− clones (clone 73 here) were analyzed by DNA N-glycosylase base release assay. ES cells were lysed, and 200 or 400 μg of cellular protein was incubated with 100 ng of UV-irradiated poly(dG-[3H]dC) for 2 or 4 h. Base release was measured by liquid scintillation counting. The results of this experiment are representative of the results obtained with all mNth1+/− clones tested.