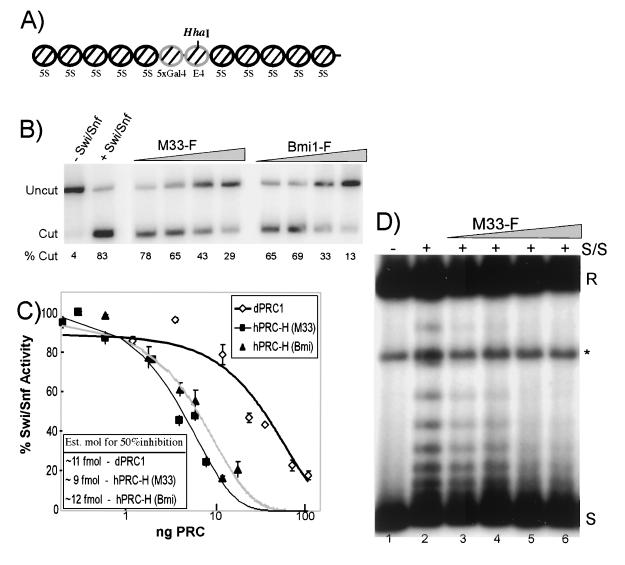
FIG. 4.
Activity of the hPRC-H complex. (A) Map of the 5S array used in the restriction enzyme and MNase assays. The HhaI site is indicated. (B) Restriction enzyme assay (REA). One nanogram (8 fmol) of nucleosomes was preincubated with increasing amounts of dPRC1 or hPRC-H from M33- and Bmi1-tagged lines. Lanes: 1, no-Swi/Snf control; 2, Swi/Snf (100 ng) only; 3 to 6, ∼0.4, 1.2, 4, and 12 fmol of hPRC-H (M33); 7 to 10, ∼1.2, 3.6, 12, and 36 fmol of hPRC-H (Bmi1). The percentage of template cut by HhaI is indicated under each lane. (C) Quantification of inhibition of remodeling. Same as panel B but with 80 fmol of nucleosomes. The amount (nanograms) of PRC added was calculated by Bradford analysis and comparative silver staining. Molar amounts were determined with an estimate of 500 kDa as the mass of hPRC-H (see Materials and Methods). Half-maximal repression occurs at ratios of hPRC-H to nucleosomes of approximately 1:8. Est. mol, estimated number of moles. (D) Topological assay. Nucleosomal plasmids were preincubated with hPRC-H for 15 min before being challenged with 100 ng of Swi/Snf and 4 U of topoisomerase I. Remodeled templates are visualized as slower-migrating topoisomers. Increasing amounts of hPRC-H increase the inhibition of Swi/Snf remodeling. Lanes: 1, no-Swi/Snf control; 2, Swi/Snf only; 3 to 6, titration of M33F hPRC-H as in panel B. R, relaxed; ∗, linear; S, fully negatively supercoiled.