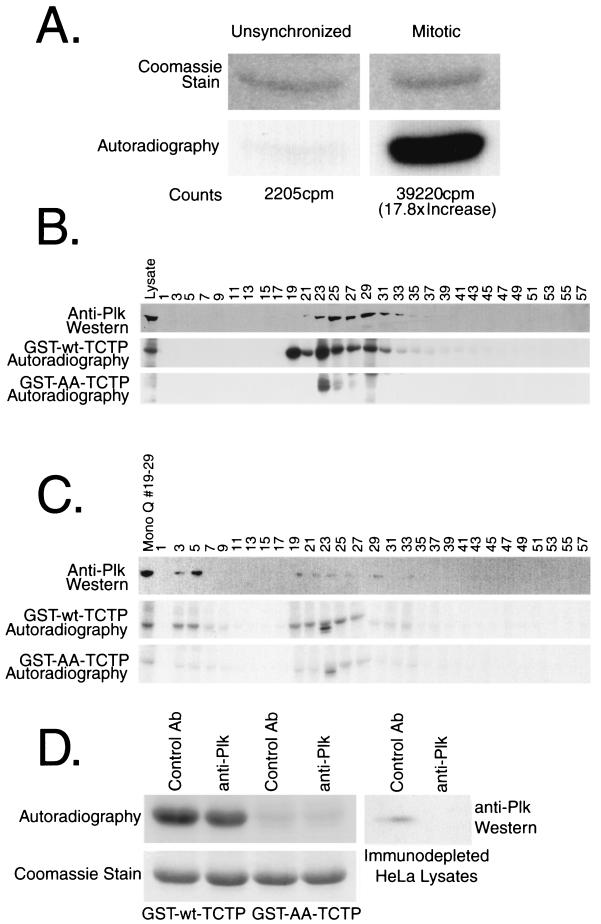
FIG. 5.
Kinase activity toward TCTP is high in mitotic lysates, and the majority cofractionates with Plk on successive MonoQ and MonoS columns. (A) Unsynchronized and nocodazole-arrested HeLa lysates were incubated with GST-TCTP on beads in an in vitro kinase reaction. The washed GST-TCTP was thrombin cleaved, and subjected to SDS-PAGE and then to autoradiography. (B) Nocodazole-arrested HeLa lysates were fractionated over a MonoQ column. The top panel is an anti-Plk blot showing the Plk elution pattern over the salt gradient. The middle and bottom panels are kinase reactions using GST-wt-TCTP and GST-AA-TCTP, respectively, to monitor the elution pattern of kinase activities toward TCTP. (C) MonoQ fractions 19 to 29 were loaded onto a MonoS column and subjected to a similar analysis as performed on the MonoQ fractions. The middle and bottom panels depict kinase reactions with each column fraction and either GST-wt-TCTP or GST-AA-TCTP, respectively, as a substrate. The top panel shows Plk fractionation as determined by Western blotting. The slightly faster-migrating band phosphorylated in fraction 23 from the MonoQ and fraction 23 from the MonoS column correspond to a contaminating protein from the lysate and not phosphorylation on GST-TCTP. (D) Immunodepletion experiments show that at least one-third of the kinase activity toward TCTP in HeLa cells is due to Plk or a Plk complex in vitro. The top panel shows kinase reactions with an equal amount of crude lysate that were immunodepleted with a control antibody (anti-Myc or anti-Mek1) or with anti-Plk antibodies. The bottom panel shows the Coomassie-stained bands of GST-TCTP with the wild-type fusion protein in the left two lanes and the double-alanine mutant in the right two lanes. The right-hand panel shows the effectiveness of the Plk immunodepletions.