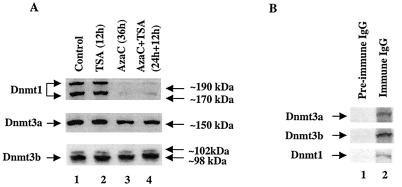
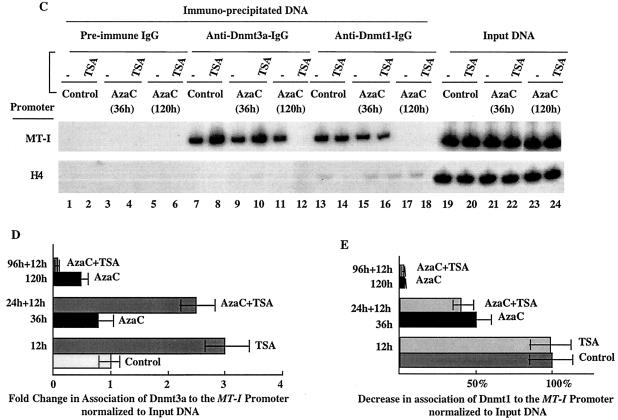
FIG. 7.
(A) Immunoblot analysis of Dnmts in the chromatin isolated from P1798 cells treated with different inhibitors. Identical amounts (100 μg) of protein of the control or treated cells were separated by SDS-PAGE on a 8% acrylamide gel, transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane, and subjected to Western blot analysis with antibodies specific for Dnmt1, Dnmt3a, and Dnmt3b. (B) P1798 cells were labeled in vivo with [35S]methionine and immunoprecipitated either with the immune IgG or preimmune IgG. Polypeptides pulled down were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by autoradiography. (C) ChIP assay with Dnmt3a and Dnmt1 antibodies. Formaldehyde cross-linked chromatin was immunoprecipitated with antibodies specific for Dnmt3a (lanes 7 to 12), Dnmt1 (lanes 13 to 18), and preimmune IgG (lanes 1 to 6). The purified DNA was amplified. The input DNA (lanes 19 to 24) used for PCR was 50-fold less than that of the amount used for immunoprecipitation. (D and E) Results of quantitative analysis of the fold change in the association of Dnmt3a and Dnmt1 to the MT-I promoter normalized to the input DNA (in three different experiments). The means ± standard errors (error bars) are shown.