FIG. 7.
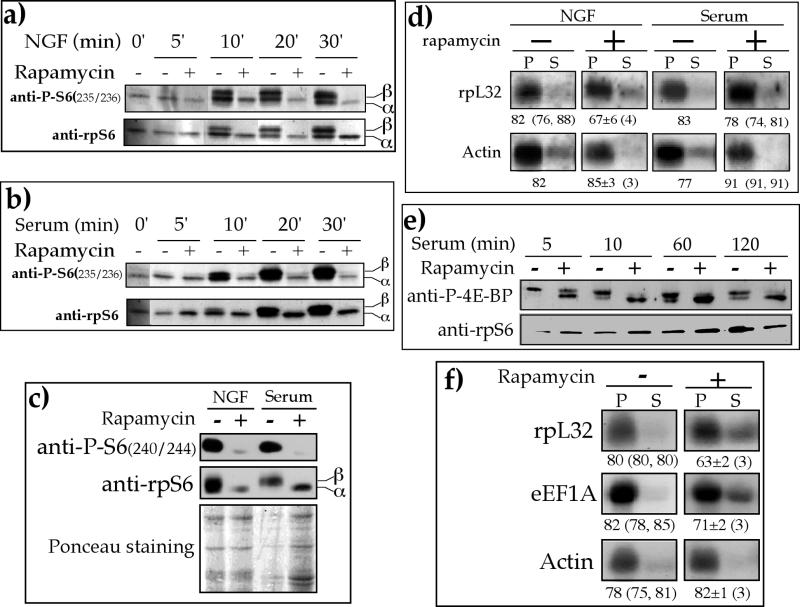
Rapamycin has a minor and delayed inhibitory effect on the translation of TOP mRNAs. (a, b, and c) PC12 cells were serum starved for 72 h (0 min) and then either treated with 50 ng of NGF per ml (a and c) or serum refed (b and c) without (−) or with (+) 20 nM rapamycin for the indicated times (a and b) or for 30 min (c), after which the cells were harvested. The cytoplasmic proteins were subjected to Western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies. The bottom panel in c is the Ponceau S-stained membrane, showing the relative protein loading among samples. (d) PC12 cells were serum starved for 72 h and then either treated with 50 ng of NGF per ml or serum refed without (−) or with (+) 20 nM rapamycin for 60 min, after which they were harvested. The polysomal distribution of the mRNAs encoding rpL32 and actin was analyzed and presented as described in the legend to Fig. 1. (e) p70S6K−/− ES cells were serum starved for 40 h and then refed in the absence (−) or presence (+) of 20 nM rapamycin for the indicated times. Cytoplasmic proteins were subjected to Western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies. (f) p70S6K−/− ES cells were serum starved for 40 h and then refed for 3 h in the absence (−) or presence (+) of 20 nM rapamycin. The polysomal distribution of the mRNAs encoding rpL32, eEF1A, and actin was analyzed as described in the legend to Fig. 1. The results in panels d and f are expressed as the average ± standard error of the mean, with the number of determinations in parentheses, or as the average, with the individual values in parentheses, if only two determinations were available.