Abstract
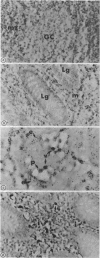
An appendix removed 15 days before onset of symptoms of subacute sclerosing panencephalitis was examined retrospectively for measles virus ribonucleic acid (RNA). Tissue sections hybridised in situ to a cloned measles virus probe of deoxyribonucleic acid specific for nucleocapsid protein showed that many cells of the lymphoid tissue contained measles virus RNA. In contrast, only a few infected lymphoid cells were detected in three out of six seropositive controls and none in three seronegative infants. A widespread chronic viral infection of the immune system, established after measles, may promote or even initiate nerve cell infection in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Horta-Barbosa L., Hamilton R., Wittig B., Fuccillo D. A., Sever J. L., Vernon M. L. Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis: isolation of suppressed measles virus from lymph node biopsies. Science. 1971 Aug 27;173(3999):840–841. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3999.840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]