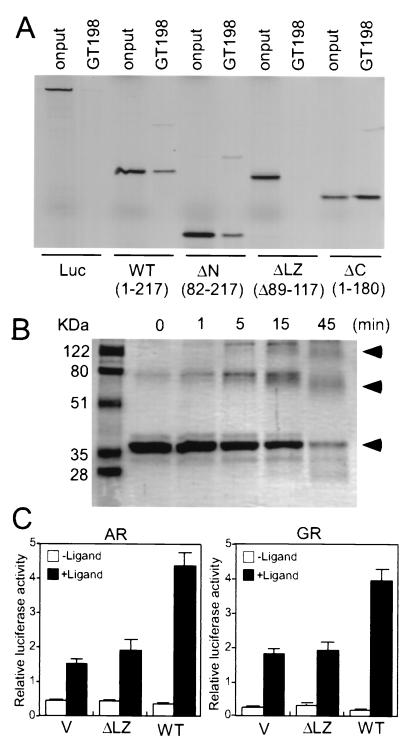
FIG. 8.
GT198 is a functional dimer. (A) Deletion of its leucine zipper abolished GT198 dimerization in vitro. Recombinant GST-GT198 fusion protein was incubated with 35S-labeled GT198 deletion fragments to detect homodimerization. Bound proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and detected by autoradiography. Luciferase (Luc) was used as a negative control. GT198 wild-type (WT) and mutants were as follows: WT (aa 1 to 217), N-terminal deletion (ΔN; aa 82 to 217), leucine zipper domain deletion (ΔLZ; Δ89–117) and C-terminal deletion (ΔC; aa 1 to 180). (B) Cross-linking of GT198. His-tagged recombinant GT198 (0.1 μg/μl) was treated with 0.15 mM glutaraldehyde for increasing amounts of time as indicated. Proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and detected by Coomassie blue staining. Arrowheads indicate the monomer, dimer, and polymer of GT198. (C) CV-1 cells were cotransfected with a GRE reporter (100 ng) and AR or GR (10 ng), along with wild-type GT198 (WT) or GT198 with the deletion at leucine zipper domain (ΔLZ; Δ89–117) or a pcDNA3 vector (V) as control. Ligand-dependent luciferase activities stimulated by 100 nM mibolerone or dexamethasone are shown as means of triplicate transfections ± standard errors.