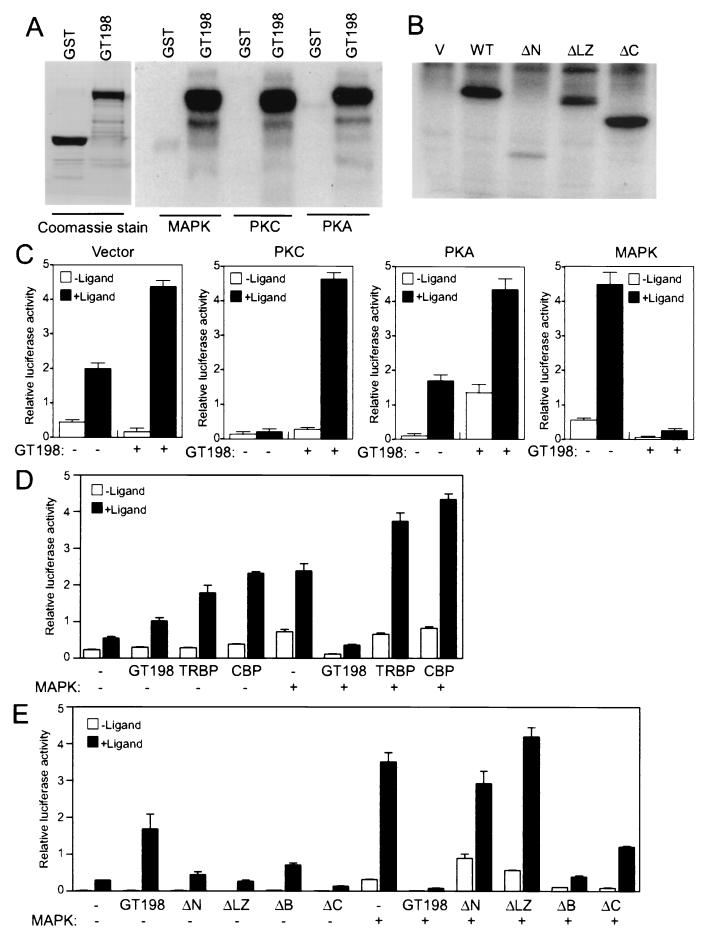
FIG. 9.
GT198 is phosphorylated and regulated by PKA, PKC, and MAPK. (A) GST-GT198 was phosphorylated in vitro by PKA, PKC, and MAPK as described in Materials and Methods. After washing, phosphorylated GST-GT198 proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and detected by autoradiography. GST alone served as a negative control. Coomassie staining of GT198 and GST proteins, shown in the left panel, was to confirm that equal amounts of protein were used. (B) 293 cells were transfected with Flag-tagged GT198 and its deletion mutants. Abbreviations are as shown in the legend to Fig. 8A. Cells were Pi labeled, and GT198 proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag M2 antibody beads (Kodak). After washing, the bound protein was separated by SDS-PAGE and visualized by autoradiography. (C) Kinase stimulation regulates GT198 coactivation function. The effects of kinases on GT198 were analyzed in CV-1 cells. Cells were cotransfected in 24-well plates with GRE-luciferase reporter (100 ng) and AR (10 ng). Coactivator GT198 or a vector control (200 ng) was cotransfected with PKA, PKC, or MAPK (20 ng) or a vector control. Cells were treated with or without 100 nM mibolerone. (D) MAPK regulation of GT198 coactivation is specific. The effects of MAPK on GT198 were analyzed in CV-1 cells with GRE-luciferase reporter (100 ng) and AR (10 ng). Coactivator GT198, TRBP, CBP, or vector control (200 ng) was cotransfected with or without MAPK (20 ng) and treated with or without the 100 nM mibolerone. (E) HeLa cells were transfected as CV-1 cells were, except that wild-type and deletion mutants of GT198 (200 ng) were used. Data shown are means of triplicate transfections ± standard errors.