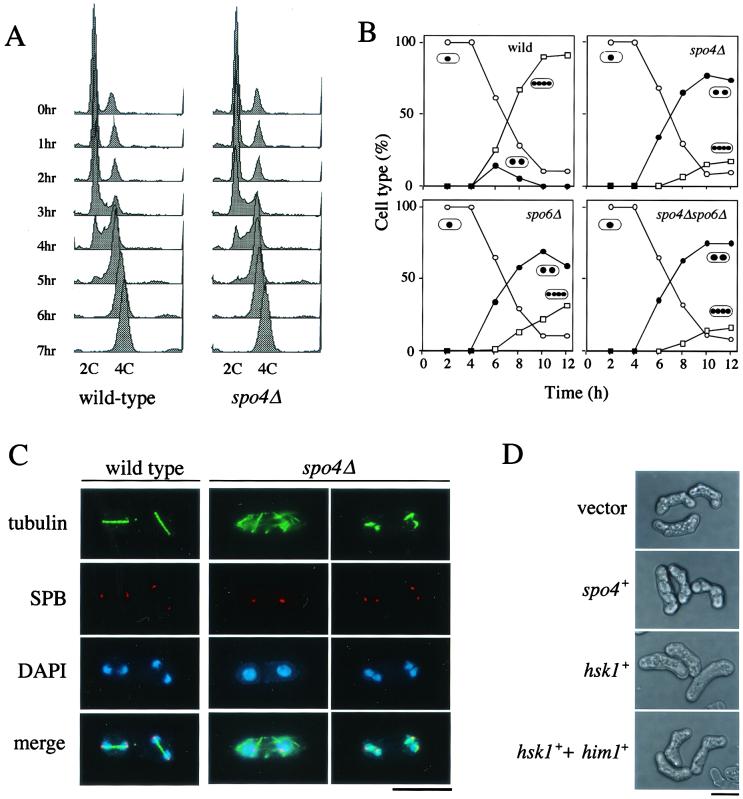
FIG. 3.
spo4+ is required for progression of meiosis II but not for the onset of premeiotic DNA synthesis. (A) Fluorescence-activated cell sorter analysis of premeiotic DNA replication in spo4Δ cells. Synchronous meiosis is induced in the diploid strains JZ670 (pat1-114/pat1-114) (wild type) and TN151 (spo4Δ pat1-114/spo4Δ pat1-114) (spo4Δ). Samples were taken every hour, and the DNA content was measured by FACScan. (B) Kinetics of meiosis in various strains. Mid-log-phase cells of wild-type (TN75), spo4Δ (TN74), spo6Δ (TN76), and spo4Δ spo6Δ (TN77) homozygous diploid strains were cultured in MM-N medium at 28°C. The progression of meiosis was monitored by DAPI staining. One, two, and four dots in ovals represent mononucleate, binucleate, and tetranucleate cells, respectively. (C) Microtubules during meiosis visualized by immunofluorescence microscopy. Diploid cells of the wild-type (TN75) and spo4Δ (TN74) strains were incubated in SSL-N sporulation medium at 28°C, sampled, and fixed. Indirect immunofluorescence microscopy was conducted using an anti-α-tubulin and an anti-Sad1 antibody to visualize microtubules and SPB (23), respectively. Bar, 10 μm. (D) Inability of Hsk1 to complement sporulation defect of the spo4 mutant. Strain TN229 (spo4-B4) was transformed with plasmids in the following combinations: pREP41 plus pREP2, pREP41(spo4) plus pREP2, pREP41(hsk1) plus pREP2, or pREP41(hsk1) plus pREP2(HA-Him1). The transformants were sporulated on SSA medium for 2 days at 28°C. HA-tagged Him1 is functional, as described by Takeda et al. (63). Bar, 10 μm.