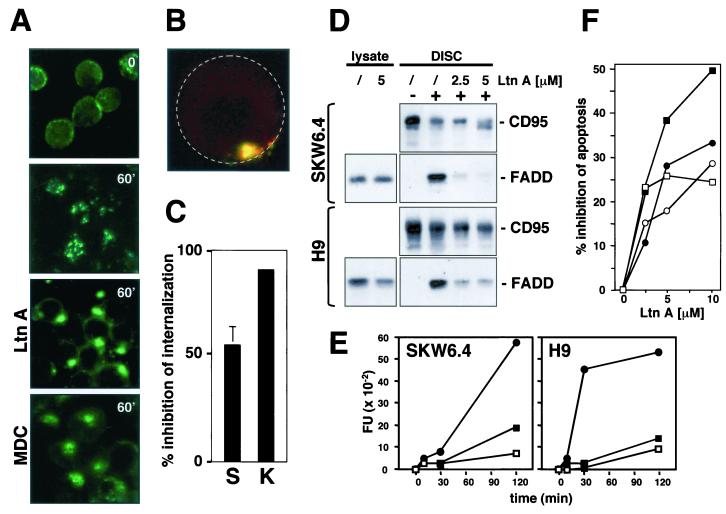
FIG. 5.
Actin filaments are required for CD95 DISC formation and receptor internalization. (A) SKW6.4 cells were left untreated or pretreated with 2.5 μM Ltn A or 100 μM MDC for 1 h at 37°C. Cells were then treated with anti-CD95 and left unstimulated (time 0) or stimulated for 60 min (60′) at 37°C as described in Fig. 2C. Samples were analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. (B) 2D projection of a 3D analysis of an Ltn A-treated SKW6.4 cell stimulated for 1 h at 37°C as described for panel A. Cells were analyzed as described in Fig. 3B. The yellow color indicates that CD95 is at the cell surface. For orientation, the outline of the cell is indicated by a stippled circle. (C) Quantification of inhibition of CD95 internalization on SKW6.4 (S) and K50 (K) cells by 5 μM Ltn A. The number of cells with 50% or more of CD95 internalized was determined as described in Materials and Methods. The experiment was done in triplicate, and the mean values with standard deviations are shown. (D) SKW6.4 or H9 cells were pretreated with Ltn A (2.5 or 5.0 μM) for 1 h at 37°C. CD95 was immunoprecipitated from either 107 untreated or anti-CD95-treated (5 min) SKW6.4 or H9 cells. Immunoprecipitates were subjected to SDS-PAGE (12% polyacrylamide) and immunoblotted with anti-FADD MAb and anti-CD95 C20. Migration positions for each protein are indicated. Cell lysates equivalent to 40 μg of protein were subjected to SDS-PAGE (12% polyacrylamide) and immunoblotted with anti-FADD antibody. (E) SKW6.4 and H9 cells were treated with 1 μg of anti-CD95 per ml for different periods of time in the absence (•) or presence of LtnA (2.5 μM [▪] or 5.0 μM [□]). Caspase 8 activity was analyzed by cleavage of the fluorogenic substrate IETD-AFC. This result was confirmed by a Western blot analysis that demonstrated reduced activation of caspase 8 in Ltn A-treated cells (data not shown). FU, fluorescence units. (F) SKW6.4 (circles) and H9 (squares) cells were preincubated with the indicated concentrations of Ltn A for 1 h and then incubated for 16 h with 1 μg of anti-CD95 (open symbols) or LZ-CD95L (solid symbols) per ml. After incubation, cells were harvested and analyzed by flow cytometry for DNA fragmentation with nuclear staining with propidium iodide. Nontoxic concentrations of Ltn A were chosen after titration of Ltn A to toxic levels. The data represent the percentage of decrease of apoptosis in the presence of Ltn A. The percentages of specific apoptosis in the absence of Ltn A were 58% (56%) and 70% (80%) for SKW6.4 and H9 cells treated with anti-CD95 (LZ-CD95L), respectively. The experiment is representative of three independent experiments.