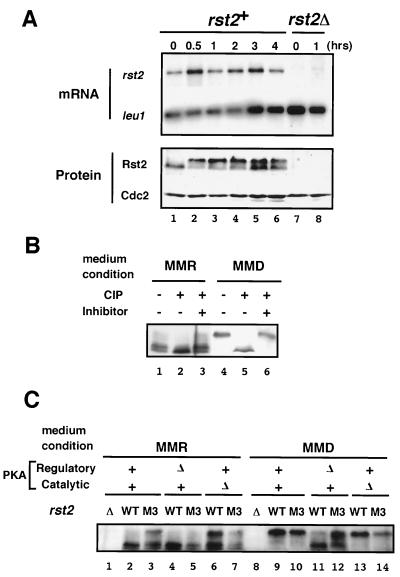
FIG. 4.
Rst2p activity is likely to be regulated posttranscriptionally. (A) Detection of rst2 mRNA and the gene product before and after a medium shift. To determine the level of rst2 mRNA, extracts were prepared from cells grown in MMD for the indicated duration, as detailed in Fig. 1. Poly(A) RNA was selected from each sample and subjected to gel electrophoresis after denaturation with formamide. We detected leu1 mRNA as an internal loading control (the time for exposure on X-ray film is much shorter than that for rst2 mRNA). For analysis of protein, boiled cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblot analysis as described in Materials and Methods. (B) Phosphatase treatment of Rst2p. Protein precipitates prepared from JY333 cells either growing in MMR or incubated in MMD for 1 h were treated with calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase (CIP), with or without the addition of the inhibitor mix, and subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblot analysis. (C) Detection of wild-type and mutated Rst2p in PKA-related mutant cells under repressing or derepressing conditions. The M3 mutant form of Rst2p lacks phosphorylatable residues at the two putative PKA-target sites. Cells of JX233 (rst2Δ), JY333 (WT), JW373 (rst2-M3), JX222 (cgs1Δ), JW374 (cgs1Δ rst2-M3), JX384 (pka1Δ), and JW377 (pka1Δ rst2-M3) were grown in MMR. A portion of each culture was shifted to MMD and incubated for 1 h. Cell lysates were prepared from the cultures in MMR and MMD and then subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblot analysis.