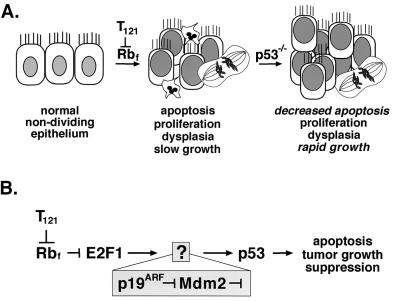
FIG. 1.
p53 tumor suppression in brain epithelium. The diagram depicts previously elucidated steps in the development of choroid plexus tumors in TgT121 mice. (A) Cell-specific expression of the T121 transgene induces proliferation of normally nondividing epithelial cells by inactivating the pRb family proteins pRb, p107, and p130. p53-dependent apoptosis is then activated, as evidenced by the 85% reduction in apoptosis in TgT121;p53−/− mice. (B) Using a genetic approach, we previously showed that E2F1 acts upstream of p53 to induce apoptosis in response to T121. Previously, E2F1 was shown to activate p19ARF transcription, and p19ARF was shown to induce p53 activities by regulating Mdm2 in cultured cells (see the introduction). In the current report, we tested whether this pathway is operative to induce p53-dependent apoptosis and suppression of brain epithelial tumors in vivo.