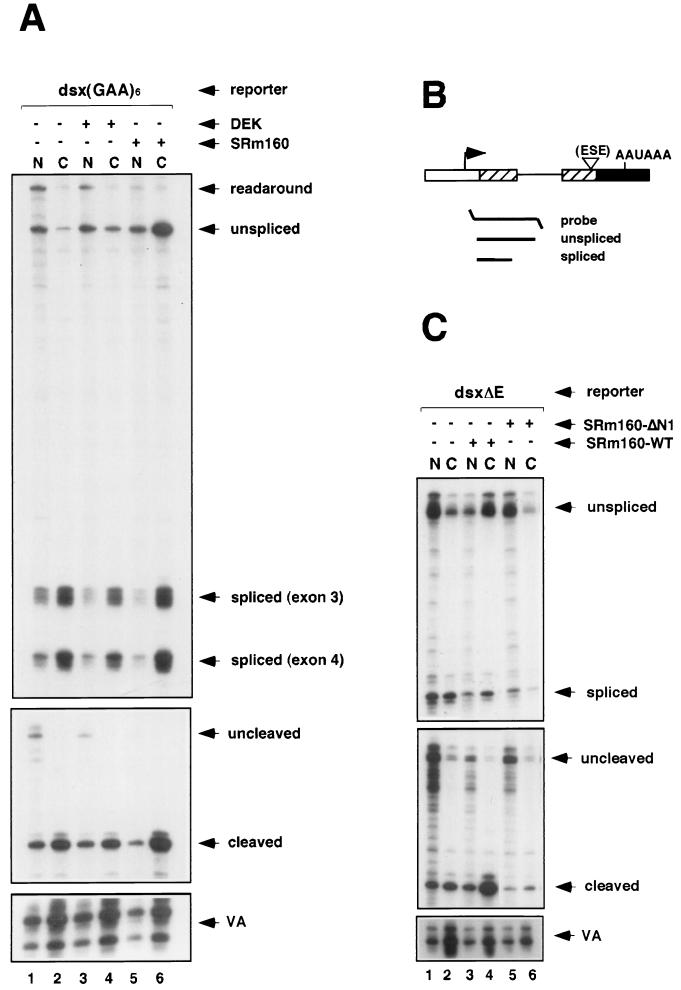
FIG. 4.
Specificity of the cleavage-stimulatory and transcript export activities of SRm160. (A) Human 293 cells were transiently transfected with the dsx(GAA)6 reporter together with a control expression vector containing no insert (pcDNA3-Flag) (lanes 1 and 2), an expression vector for HA epitope-tagged DEK (pcDNA3-DEK) (lanes 3 and 4), or an expression vector for Flag epitope-tagged SRm160 (pcDNA3-fSRm160) (lanes 5 and 6); the pol III reporter (pSPVA) was cotransfected in each case as an internal control. Proportional amounts of RNA isolated from the nuclear (N) and cytoplasmic (C) fractions of the transfected cells were analyzed by RNase protection using either a splicing protection probe or the 3′-end protection probe (refer to the legend to Fig. 2). The identity of each RNA species is indicated. (B) Schematic representation of the short splicing RNase protection probe used to analyze splicing of transcripts from the dsxΔE reporter. The predicted RNase protection products are shown below each probe (for sizes refer to Materials and Methods and supplementary information available at http://www.utoronto.ca/intron/supp_info). (C) Human 293 cells were transiently transfected with the dsxΔE reporter together with a control expression vector containing no insert (pcDNA3-Flag) (lanes 1 and 2), an expression vector for Flag epitope-tagged SRm160 (pcDNA3-fSRm160) (lanes 3 and 4), or an expression vector for Flag epitope-tagged SRm160 deleted from amino acids 1 to 155 (pcDNA3-fSRm160ΔN1) (lanes 5 and 6); the pol III reporter (pSPVA) was cotransfected in each case as an internal control. Proportional amounts of RNA isolated from the nuclear (N) and cytoplasmic (C) fractions of the transfected cells were analyzed by RNase protection using either the short splicing protection probe or the 3′-end protection probe. The identity of each RNA species is indicated.