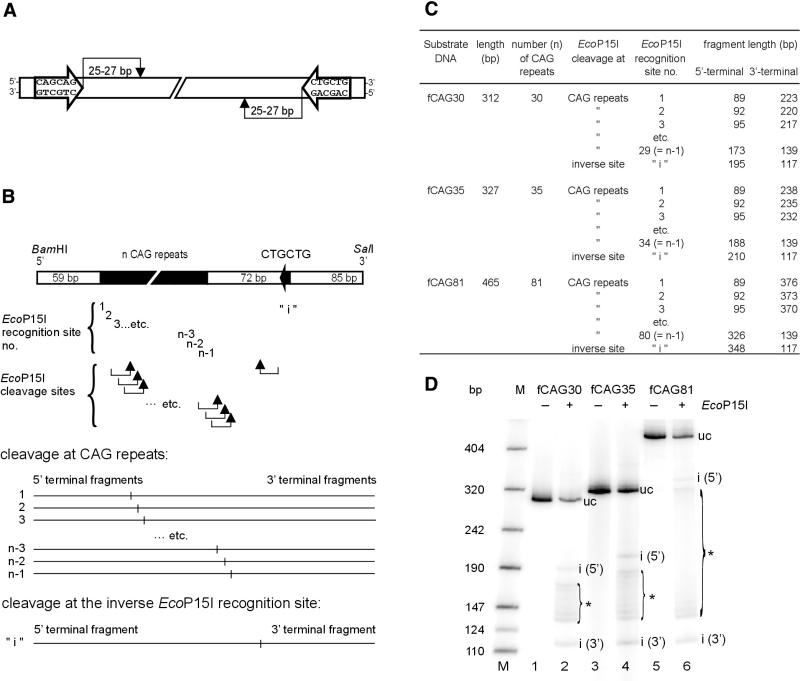
Figure 1.
EcoP15I cleavage of DNA substrates that contain CAG repeats of different lengths. (A) Recognition and cleavage sites of restriction endonuclease EcoP15I in the DNA molecule. For DNA restriction, the enzyme needs two 5′-CAGCAG sequences being inversely oriented in the double-stranded DNA. Cleavage occurs 25–27 bp downstream of one of the two inverted sites (see Introduction). (B) General chart of the used DNA substrates that contain a number of n CAG repeats and an additional inverse EcoP15I recognition site 5′-CTGCTG at a distance of 72 bp from the 3′-end of the CAG repeats. Two CAG trinucleotides correspond to one EcoP15I recognition site 5′-CAGCAG. Thus, an expansion of n CAG trinucleotides results in a series of (n-1) EcoP15I recognition sites that overlap by 3 bp. Arrows indicate the EcoP15I cleavage sites 25–27 bp downstream of the various recognition sites. In the lower part of the chart the fragment patterns expected from cleavage either at one of the CAG repeats or at the inverse EcoP15I recognition site ‘i’ are schematically shown. (C) Calculated lengths of the DNA fragments expected from EcoP15I cleavage of the DNA substrates fCAG30, fCAG35 and fCAG81. Fragment lengths are assigned to the corresponding EcoP15I recognition sites nos 1 to (n-1) within the CAG repeats or to the inverse site ‘i’. (D) EcoP15I cleavage patterns of the DNA substrates fCAG30, fCAG35 and fCAG81. The DNA substrates were radioactively labeled at both ends. Each substrate (50 fmol) was incubated in the presence or absence of a 10-fold molar excess of EcoP15I enzyme over DNA substrate at 37°C for 30 min. Cleavage was analyzed on a non-denaturing 5% (w/v) polyacrylamide gel as described in the Materials and Methods. The ladders of EcoP15I cleavage fragments were marked by brackets. M, molecular weight marker; uc, uncleaved DNA substrates; i (5′), 5′-terminal DNA fragment after EcoP15I cleavage at the inverse EcoP15I recognition site; i (3′), 3′-terminal DNA fragment after EcoP15I cleavage at the inverse EcoP15I recognition site; *, DNA fragments generated by EcoP15I cleavage at EcoP15I recognition sites nos 1 to (n-1) within the CAG repeats.