Figure 3.
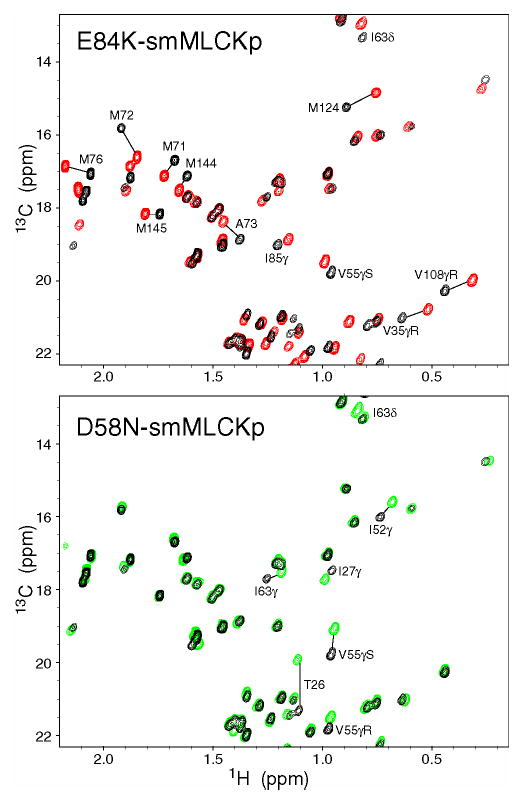
Chemical shift-based identification of structural perturbations in the CaM-smMLCKp complex introduced by various mutations in calmodulin. Shown are superpositions of the 13C-1H chemical shift correlation maps for the wild-type CaM-smMLCKp (black) and E84K-smMLCKp (red); wild-type CaM-smMLCKp (black) and D58N-smMLCKp (green). Many methyl groups throughout the E84K-smMLCKp complex, including all methionines, experience large chemical shift changes as a result of the mutation. D58N-smMLCKp is a more moderate case, where chemical shift perturbations are localized to Ca2+-binding loops I and II and helix C.
