Abstract
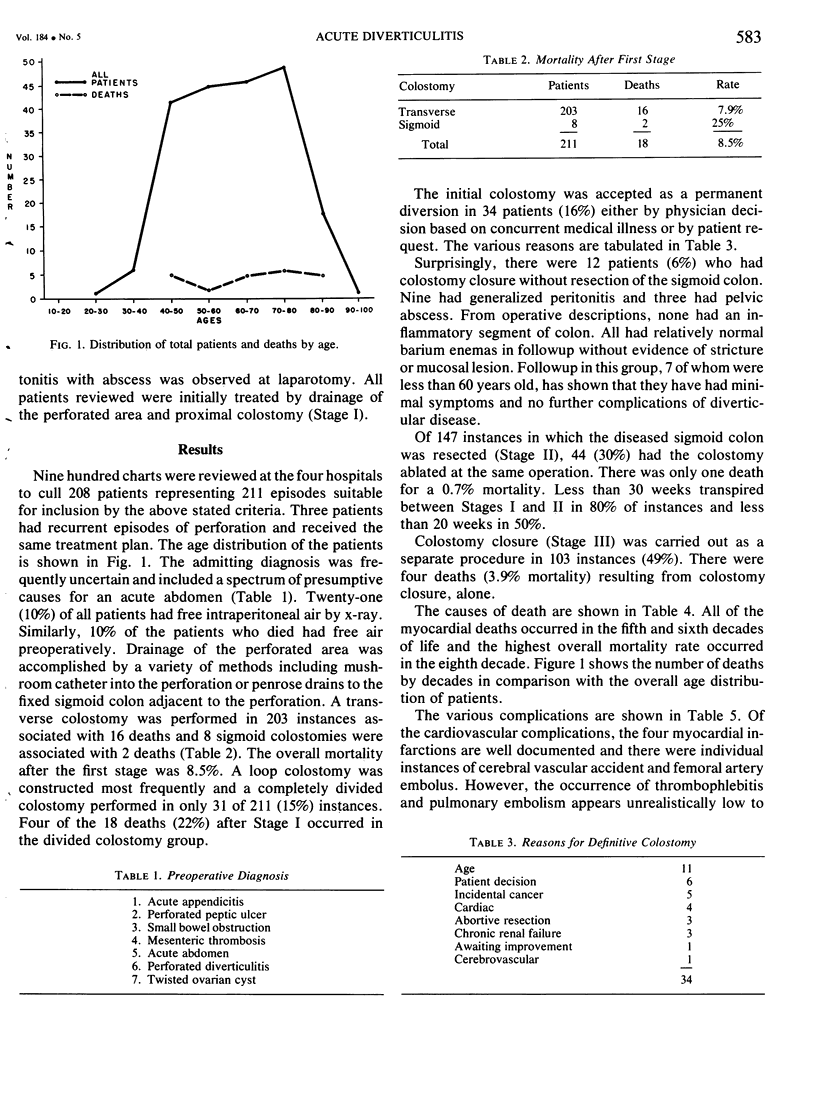
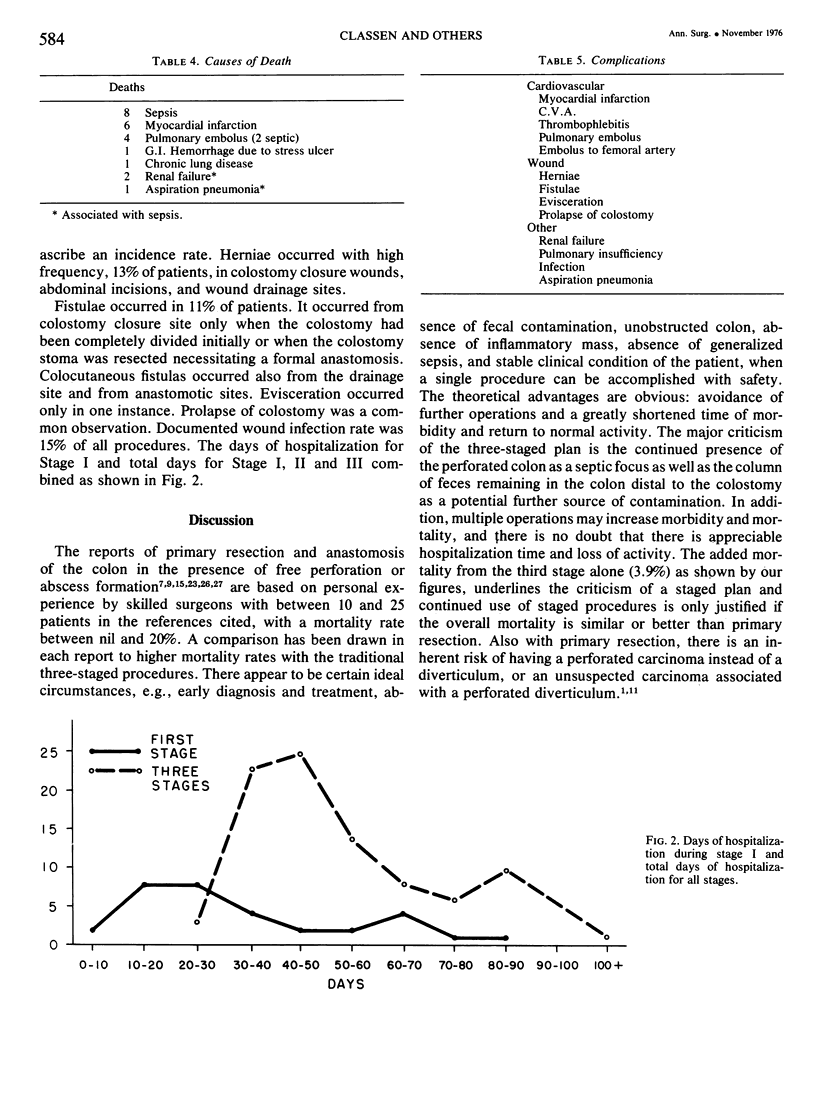
A retrospective 10-year experience with the traditional three-stage plan (diverting colostomy, resection, colostomy closure) for perforated diverticulitis of the colon in four urban hospitals was reviewed to accurately assess the mortality rate. Only patients who were admitted in a non-elective manner with signs of an acute abdomen or who were already hospitalized with another illness and developed an acute abdomen were considered. Fecal or generalized purulent peritonitis, or pelvic peritonitis with abscess were observed at laparotomy in all instances. Two hundred and eight patients representing 211 episodes met the above stated criteria for inclusion in the study. A transverse colostomy was performed in 203 instances associated with 16 deaths, and 8 sigmoid colostomies were associated with two deaths. The overall mortality after the first stage was 8.5%. A loop colostomy was constructed most frequently and a completely divided colostomy performed in only 31 of 211 (15%) instances. Of 147 instances in which the diseased sigmoid colon was resected, 44 (30%) had the colostomy ablated at the same operation, resulting in only one death (0.7% mortality). Colostomy closure as a separate procedure in 103 instances resulted in 4 deaths (3.9% mortality). The highest mortality rate occurred in patients in the in the eighth decade. Staged procedures for perforated colonic diverticula can be carried out with a mortality rate of 11%.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacon H. E., Tse G. N., Herabat T. Coexisting carcinoma with peridiverticulitis of the colon. Dis Colon Rectum. 1973 Nov-Dec;16(6):500–503. doi: 10.1007/BF02588877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barabas A. P. Peritonitis due to diverticular disease of the colon: review of 44 cases. Proc R Soc Med. 1971 Mar;64(3):253–254. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman L. G., Burdick D., Heitzman E. R., Prior J. T. A critical reappraisal of sigmoid peridiverticulitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1968 Sep;127(3):481–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolt D. E., Hughes L. E. Diverticulitis: a follow-up of 100 cases. Br Med J. 1966 May 14;1(5497):1205–1209. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5497.1205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botsford T. W., Zollinger R. M., Jr, Hicks R. Mortality of the surgical treatment of diverticulitis. Am J Surg. 1971 Jun;121(6):702–705. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(71)90050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne J. J., Garick E. I. Surgical treatment of diverticulitis. Am J Surg. 1971 Apr;121(4):379–384. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(71)90226-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne R. V. Primary resection of the colon for perforated diverticulum. Am J Surg. 1966 Aug;112(2):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(66)90019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colcock B. P. Complications of diverticulitis. Am Surg. 1971 Mar;37(3):121–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dandekar N. V., McCann W. J. Primary resection and anastomosis in the management of perforation of diverticulitis of the sigmoid flexure and diffuse peritonitis. Dis Colon Rectum. 1969 May-Jun;12(3):172–175. doi: 10.1007/BF02617805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giffin J. M., Butcher H. R., Jr, Ackerman L. V. Surgical management of colonic diverticulitis. Arch Surg. 1967 May;94(5):619–626. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1967.01330110035005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn F., McSherry C. K. Obstruction and perforation in colo-rectal cancer. Ann Surg. 1971 Jun;173(6):983–992. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197106010-00017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves H. A., Jr, Franklin R. M., Robbins L. B., 2nd, Sawyers J. L. Surgical management of perforated diverticulitis of the colon. Am Surg. 1973 Mar;39(3):142–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy S. B., Fitts W. T., Jr, Lench J. B. Surgical treatment of diverticular disease of the colon: evaluation of an eleven-year period. Ann Surg. 1967 Dec;166(6):947–954. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196712000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden J. L. Primary resection and anastomosis in the treatment of perforated lesions of the colon. Am Surg. 1965 Dec;31(12):781–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSherry C. K., Grafe W. R., Jr, Perry H. S., Glenn F. Surgery of the large bowel for emergent conditions. Staged vs primary resection. Arch Surg. 1969 Jun;98(6):749–753. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1969.01340120097015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. W., Jr, Wichern W. A., Jr Perforated sigmoid diverticulitis. Appraisal of primary versus delayed resection. Am J Surg. 1971 May;121(5):536–540. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(71)90134-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitty W. F., Befeler D., Grossi C., Rousselot L. M. Surgical management of complications of diverticulitis in patients over seventy years of age. Am J Surg. 1969 Feb;117(2):270–277. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(69)90314-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley R. V., Ross F. P. Sigmoid diverticulitis: evaluation of current practice in a community hospital. Ann Surg. 1966 Aug;164(2):275–283. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196608000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly M. C. Colonic diverticula. Surgical management. Br Med J. 1970 Sep 5;3(5722):570–573. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5722.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodkey G. V., Welch C. E. Surgical management of colonic diverticulitis with free perforation or abscess formation. Am J Surg. 1969 Feb;117(2):265–269. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(69)90313-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roxburgh R. A., Dawson J. L., Yeo R. Emergency resection in treatment of diverticular disease of colon complicated by peritonitis. Br Med J. 1968 Aug 24;3(5616):465–466. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5616.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan P. Emergency resection and anastomosis for perforated sigmoid diverticulitis. Aust N Z J Surg. 1974 Feb;44(1):16–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.1974.tb06511.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smiley D. F. Perforated sigmoid diverticulitis with spreading peritonitis. Am J Surg. 1966 Mar;111(3):431–434. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(66)80022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolins S. H. Surgical treatment of diverticulitis. Experience at a large Municipal Hospital. JAMA. 1975 May 26;232(8):830–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins G. L., Oliver G. A. Surgical treatment of acute perforative sigmoid diverticulitis. Surgery. 1971 Feb;69(2):215–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan C. S., Furcinitti J. F., Lavarreda C. Surgical management of perforated lesions of the colon with diffusing peritonitis. Am J Surg. 1971 Apr;121(4):374–378. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(71)90225-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


