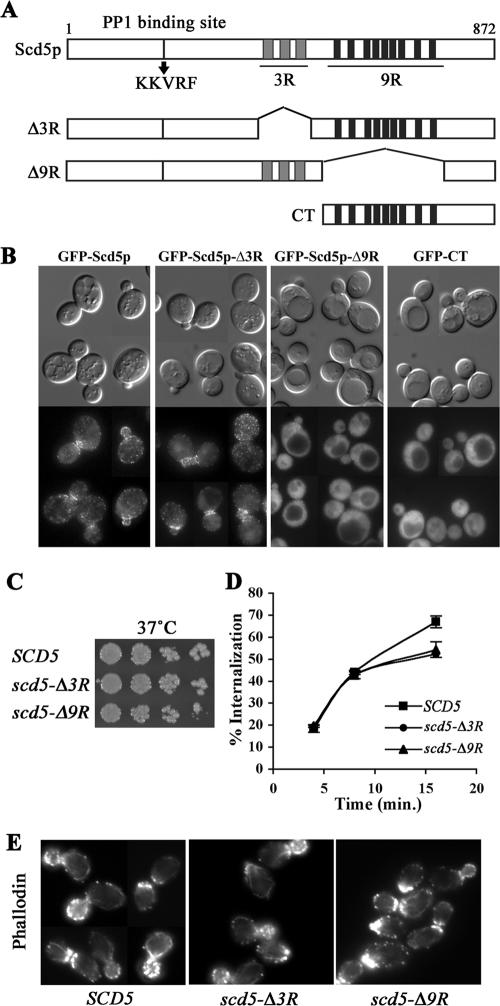
Figure 1.
The 9R is necessary for cortical localization of Scd5p, but growth, actin organization, and endocytosis are relatively normal in scd5-Δ9R. (A) Schematic diagram of Scd5p and deletion mutants. Scd5p contains a PP1-binding site (KKVRF), three repeats of 20 amino acids (3R; gray boxes), and nine repeats of 12 amino acids (9R; black boxes). (B) Localization of GFP-tagged Scd5p and deletion mutants: scd5Δ cells expressing GFP-Scd5p (SL4702), GFP-Scd5p-Δ3R (SL4645) or GFP-Scd5p-Δ9R (SL4683), and SCD5 cells expressing GFP-CT (SL4675) were examined by fluorescence microscopy at 25°C. Similar results were observed after shift to 37°C (unpublished data). (C) Growth: wild-type (SL4706), scd5-Δ3R (SL4708), and scd5-Δ9R (SL4709) cells were serial diluted, spotted on YEPD plates, and grown for 3 d at 37°C. (D) Receptor-mediated endocytosis: wild-type SCD5 (SL4436), scd5-Δ3R (SL4738), and scd5-Δ9R (SL4741) cells were preincubated at 37°C for 15 min and then pulsed with 35S-labeled-α-factor. Samples were collected at indicated time points for determination of percent of cell-associated α-factor internalized. (E) Actin staining: wild-type (SL4418), scd5-Δ3R (SL4403), and scd5-Δ9R (SL4704) cells were grown to log-phase in YEPD at 25°C and shifted to 37°C for 2 h before fixation. Filamentous actin was stained with Alexa-568 phalloidin.