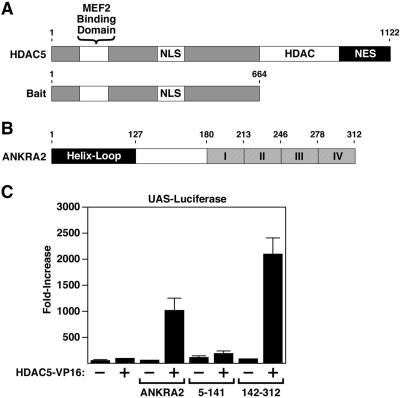
Figure 1.
Association of HDAC5 with ANKRA2 in yeast and mammalian cells. (A) Human HDAC5 is 1122 amino acids in length and contains a MEF2-binding domain, nuclear localization, and nuclear export sequences (NLS and NES, respectively) and a histone deacetylase catalytic domain (HDAC). The amino-terminal half of HDAC5 was used as bait in a yeast two-hybrid screen. (B) HDAC5 bait interacted with multiple clones of prey encoding ANKRA2. ANKRA2 is a 312-amino acid protein that contains an amino-terminal helix-loop domain and four carboxy-terminal ankyrin repeats (I-IV). (C) A mammalian two-hybrid system was used to confirm the interaction between HDAC5 and ANKRA2. COS cells were transfected with a luciferase reporter gene driven by five GAL4 DNA-binding sites (UAS-Luciferase), and the indicated combinations of vectors encoding amino acids 1-664 of HDAC5 fused to the VP16 transcriptional activation domain (HDAC5-VP16) and the GAL4 DNA-binding domain fused to either full-length ANKRA2 (ANKRA2), the amino-terminal half of ANRKA2 (5-141), or the carboxy-terminal half of ANKRA2 (142-312). Increased luciferase activity indicates that the GAL4-ANKRA2 construct recruited HDAC5-VP16 to the promoter of the luciferase reporter.