Figure 4.
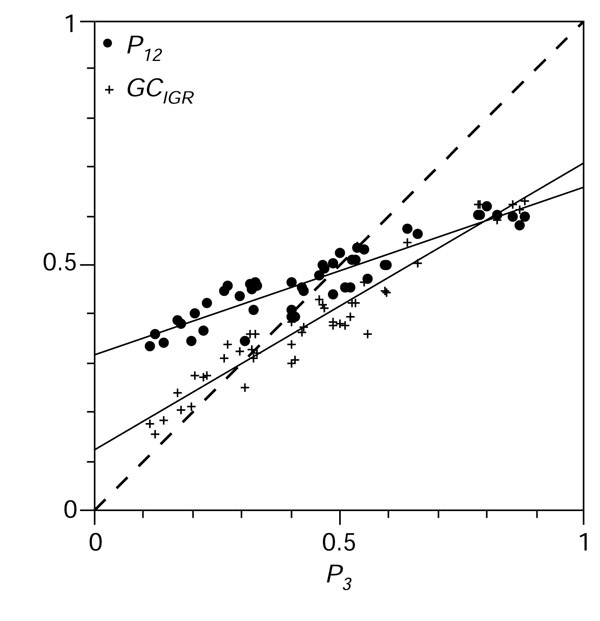
Distribution of G+C content in the dataset. The G+C content of the 51 bacterial chromosomes under analysis was highly variable from 25.5% in the Ureaplasma urealyticum chromosome to 67.9% in Halobacterium sp., with a larger distribution in third codon positions (x-axis P3 from 11.2% to 88.0%) than in intergenic spaces (y-axis GCIGR from 15.5% to 63.4%) than in first and second position (y-axis P12 from 33.4% to 62.2%) as expected [10,11]. Regression slopes (or ε values) and their standard deviations for P12 and GCIGR were 0.343 ± 0.021 and 0.586 ± 0.024, respectively.
