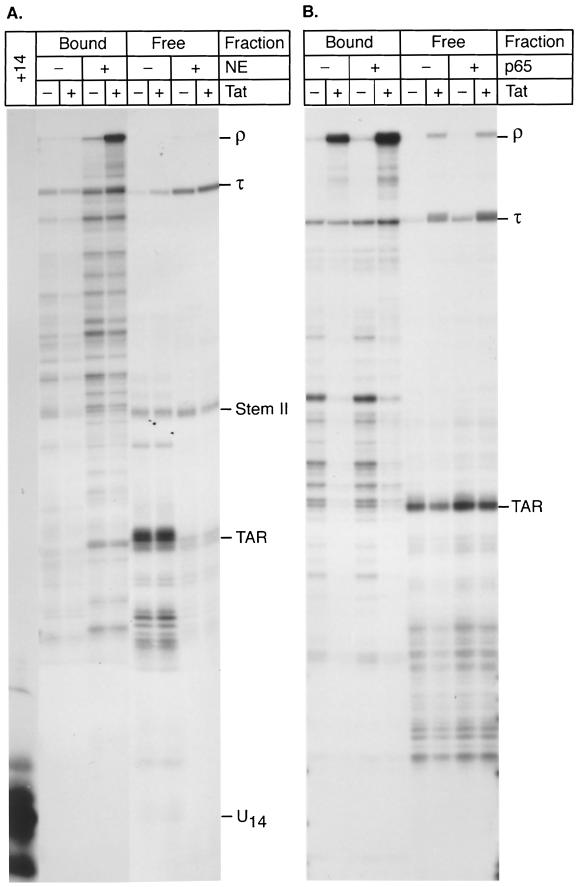
FIG. 2.
Efficient elongation from transcription complexes paused at +14 requires the addition of nuclear extract. (A) Preinitiation complexes were set up on immobilized templates as described in the legend to Fig. 1 and paused at +14 by elongation in the presence of CTP, GTP, and [α-32P]UTP. The +14 products were then washed and chased by addition of unlabeled nucleotides. Reactions were performed in the absence (−) or presence (+) of 10 μl of fresh nuclear extract (NE) and of 20 ng of Tat protein. RNA products tightly associated with the elongation complexes (bound) or prematurely released from the template (free) were analyzed: Abbreviations: TAR, paused transcription complexes or transcripts released at +59, at the end of the TAR stem-loop structure; Stem II, complexes released at +104, at the end of stem-loop II in the HIV sequence; τ, paused transcription complexes or transcripts released at the terminator; ρ, transcripts reaching the end of the template. (B) Transcription in the presence of NF-κB. Recombinant NFκB p65 protein (300 ng) purified from baculoviruses (+) or the corresponding storage buffer (NDBZ buffer; see Materials and Methods) (−) was added prior to the nuclear extract to set up the preinitiation complex. Transcription was then carried out to pause the complexes at+14, and beads were washed and then chased in the presence of fresh nuclear extract and the absence (−) or presence (+) of 20 ng of Tat. Bound or released (free) RNA products were analyzed.