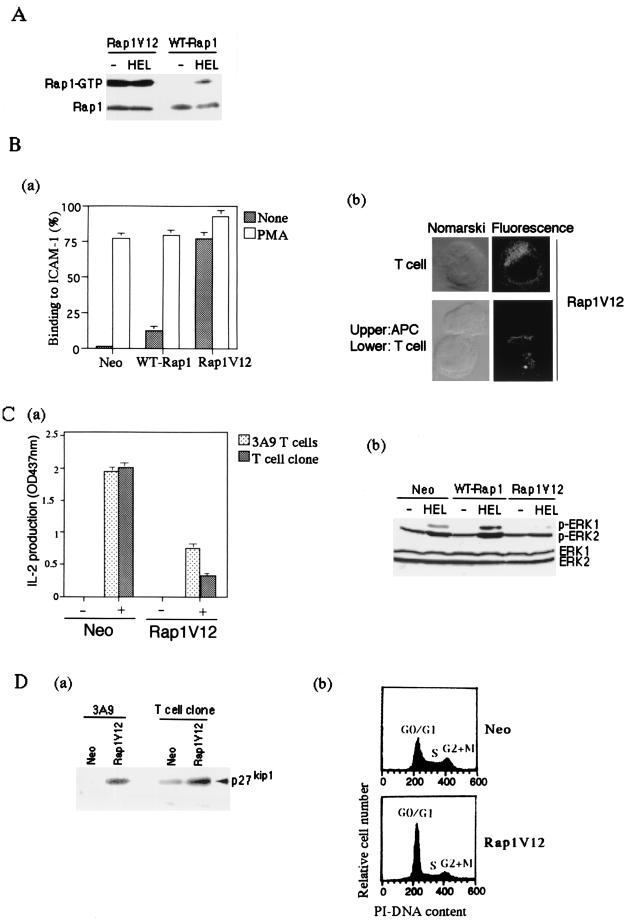
FIG. 7.
Suppression of IL-2 production and accumulation of p27Kip1 by Rap1V12. (A) Level of Rap1-GTP in Rap1V12- and WT-Rap1-expressing cells. 3A9 T cells expressing T7-tagged Rap1V12 and WT-Rap1 were cultured with CH27 B cells without (−HEL) or with antigen (+HEL) for 8 h. GTP-bound Rap1 was analyzed as in Fig. 1B with pull-down of GST-RalGDS-RBD. Bound Rap1 (upper) and total Rap1 (lower) were detected by Western blotting with anti-T7 antibody. (B) Rap1V12 increased LFA-1-ICAM-1-mediated adhesion of 3A9 T cells and accumulated at the contact site with APC in the absence of antigen. (Ba) Adhesion of 3A9 T cells transfected with vector alone, WT-Rap1, and Rap1V12. T cells were stimulated with or without 10 ng of PMA per ml for 30 min at 37°C in mouse ICAM-1-Ig-coated plates and analyzed as described in Materials and Methods. The average and standard errors of triplicate experiments are shown. (Bb) Cellular localization of Rap1V12. 3A9 T cells expressing T7-tagged Rap1V12 were mixed with CH27 B cells for 30 min at 37°C and immunostained with anti-T7 antibody and Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-mouse IgG (Molecular Probes). Representative confocal images of Rap1V12 in T cells either unconjugated or conjugated with CH27 B cells are shown. The left panels are Nomarski views of the same cells shown for Rap1V12 in the right panels. Cells transfected with vector alone did not show any significant fluorescent signals under the same conditions. (C) Persistent and marked preactivation of Rap1 rendered T cells unresponsive to antigen. (Ca) Decreased IL-2 production in Rap1V12-expressing 3A9 T cells and OVA-specific T-cell clone. 3A9 T cells and the OVA-specific T-cell clone transfected with vector alone (Neo) or Rap1V12 were cultured with appropriate APC, as in Fig. 3 and 4, with (+) or without (−) antigen for 16 h. IL-2 concentrations of the supernatants were measured. An optical density at 437 nm of 1 was equal to 0.23 ng of recombinant mouse IL-2/ml. Bars represent the average and standard error of two representative experiments performed in triplicate. (Cb) Antigen-induced phosphorylation of ERKs in 3A9 T cells expressing Rap1V12 or WT-Rap1. 3A9 T cells transfected with the neomycin genes (Neo), WT-Rap1, and Rap1V12 were cultured for 1 h with CH27 B cells which were preloaded without (−HEL) or with antigen (+HEL) for 16 h and fixed with 1% paraformaldehyde. The phosphorylation levels of ERKs were examined by Western blotting with antiphosphorylated ERK1 (pERK1)- and ERK2 (pERK2)-specific antibodies (upper panel). The expression levels of total ERK1 and ERK2 are shown (lower panel). (D) Accumulation of p27Kip1 and cell cycle arrest in Rap1V12-expressing T cells. (Da) Increased expression levels of p27Kip1 in Rap1V12-expressing 3A9 T cells and OVA-specific T-cell clone were detected by Western blotting with anti-p27Kip1 antibody. (Db) Increased cell population in the G0/G1 phase caused by Rap1V12 expression. The OVA-specific T-cell clones transfected with vector alone (Neo) or Rap1V12 were stained with PI and analyzed by flow cytometry.